Fig. 3.
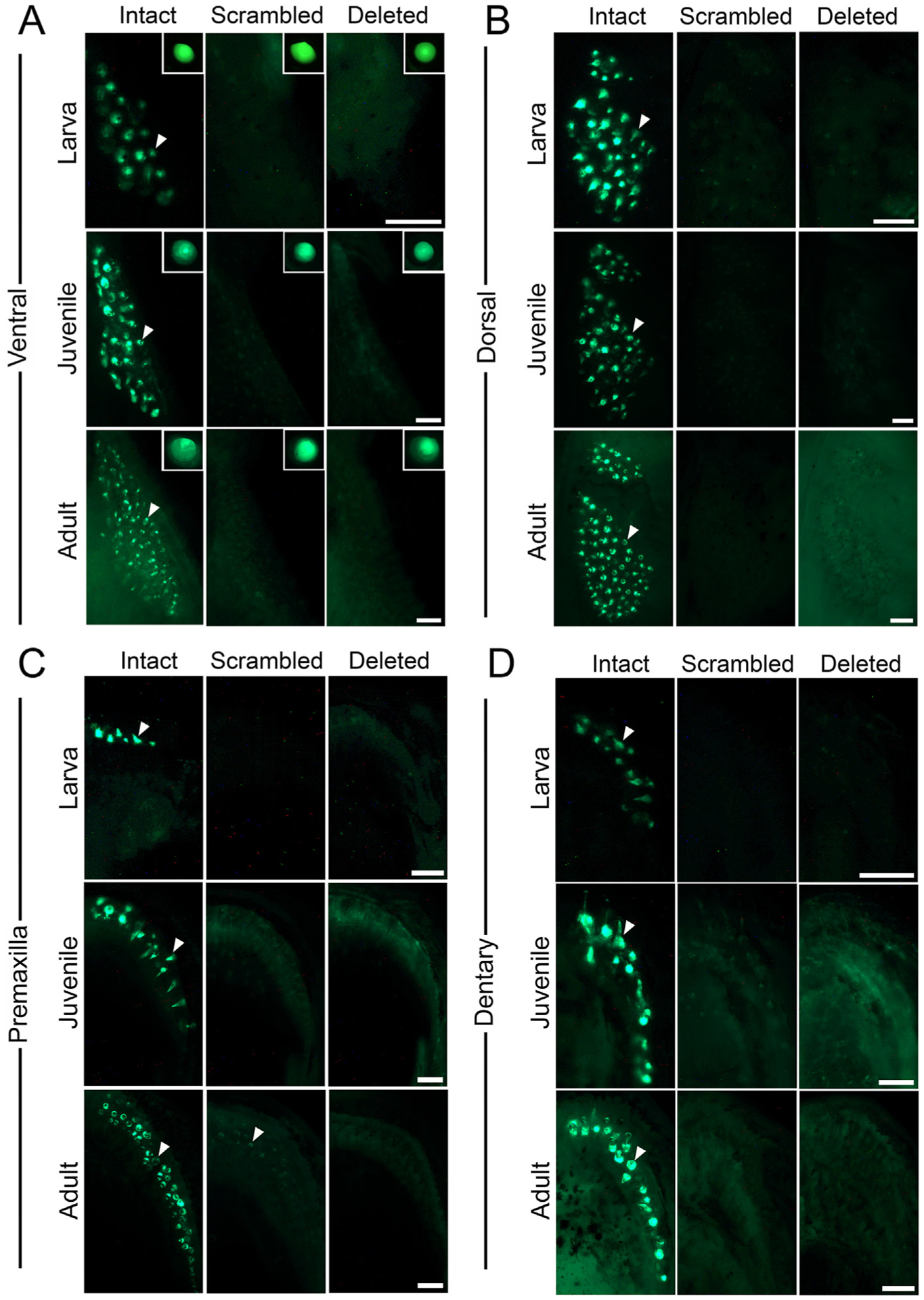
Predicted Foxc1 binding site is required for pharyngeal and oral tooth expression in larva, juveniles, and adults. GFP reporter gene expression in ventral (A,D) and dorsal (B,C) pharyngeal (A,B) and oral (C,D) jaws in larva (7–11 mm SL), juvenile (17–21 mm SL), and adult (37–55 mm SL) sticklebacks. GFP expression was detected in the epithelium and mesenchyme of developing teeth (arrowheads) in larva, juvenile, and adult stages with the intact sequence of the predicted Foxc1 binding site (left columns). No expression was detected in any developing teeth of larva, juvenile, and adults with the scrambled or deleted sequence of the predicted Foxc1 binding site (middle and right columns, respectively), except for faint expression in some adult premaxilla teeth (arrow in adult premaxilla panel in C). (A insets) Lens of eye with GFP expression as an internal control driven by the hsp70l promoter used in the transgenic construct. Scale bars = 100 μm (larva and juvenile), 250 μm (adult).
