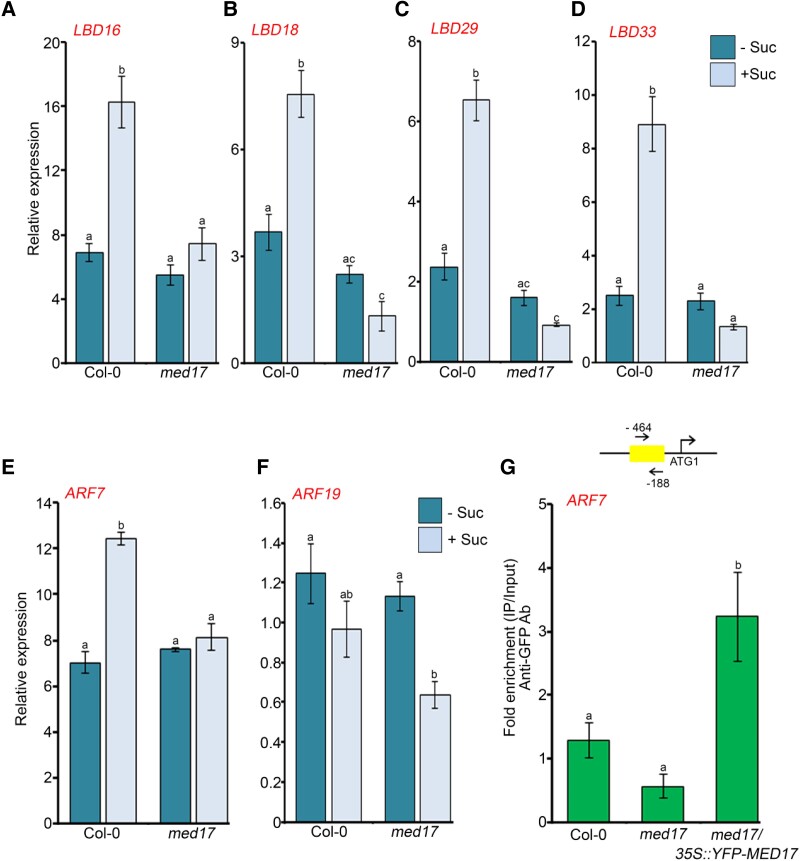
Figure 5.
MED17 is required for sucrose-triggered expression of auxin signaling genes. A–D, RT-qPCR showing expression of auxin-responsive LBD genes (LBD16, LBD18, LBD29, and LBD33) after sucrose treatment. E, F, RT-qPCR showing expression of auxin-responsive TF genes (ARF7 and ARF19) after sucrose treatment. In (A–F), 7-day-old Col-0 and med17 seedlings were treated with 90 mM sucrose for 3 h. Gene expression values were calculated as ΔCt. RT-qPCR analysis was performed on three independent biological replicates (n = 3). Bar plots represent mean values, and error bars denote Se. Statistical difference has been depicted by P-value as assessed by one-way ANOVA and Tukey's HSD post hoc test. G, ChIP-qPCR showing enrichment of YFP-MED17 at the promoter of ARF7 in 7-day-old Col-0, med17, and med17/35S:YFP-MED17 seedlings. Promoter region of ARF7 harboring E2F-binding element was amplified. Positions of the amplicon relative to ATG are shown in the upper panel. Ct values with and without antibody samples were normalized to input control. Untransformed Col-0 and med17 seedlings were taken as negative control. YFP-MED17 binding on promoters was calculated as fold enrichment. ChIP-qPCR analysis was performed on three technical replicates (n = 3) from a single representative experiment. Experiments were independently repeated twice (biological replicates; n = 2). Bar plots represent mean values, and error bars denote Sd. Statistical difference has been depicted by P-value as assessed by one-way ANOVA and Tukey's HSD post hoc test. For all the graphs, P-value of 0.05 or lower (P ≤ 0.05) was considered statistically significant, whereas P-value greater than 0.05 (P > 0.05) was considered non-significant (ns).