Figure 5.
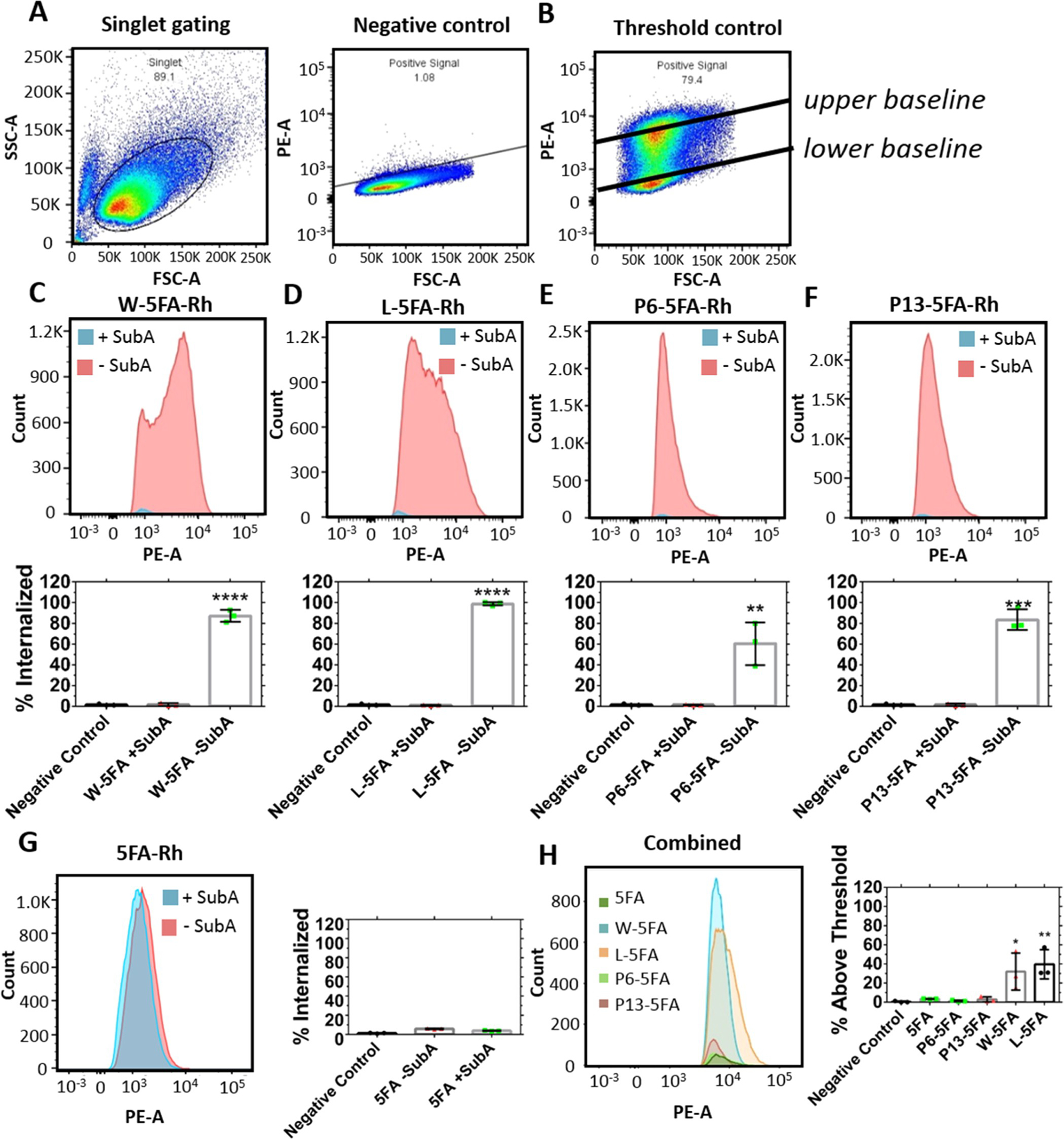
W-5FA and L-5FA undergo csGRP78-dependent cell association by flow cytometry. Internalization of rhodamine-labeled W, L, P6, and P13 fused to 5FA was evaluated in BT474 cells treated with and without SubA (0.2 μg/mL). (A) Unstained negative control was used to define a lower gating baseline for detectable cell association, while an (B) untargeted rhodamine-labeled control (5FA) at 20 μM defined an upper gating baseline for higher cell association. (C–F) Cells treated with or without SubA were treated with X-5FA (5 μM). Signal was cutoff below the lower baseline to show that control cells retained significantly more signal, while cells treated with SubA were indistinguishable from the negative controls. (G) Untargeted 5FA (5 μM) internalization is low relative to targeted X-5FA and was minimally affected by treatment with SubA. (H) To compare between positive internalization data, the signal below the 95th percentile of the upper gating baseline (20 μM 5FA) was cutoff in samples A–G to clarify differences between groups. Internalization of W and L-5FA was significantly higher than that of P6 and P13–5FA. Mean ± SD (n = 3). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.005, ***p < 0.0005, and ****p < 0.00005.
