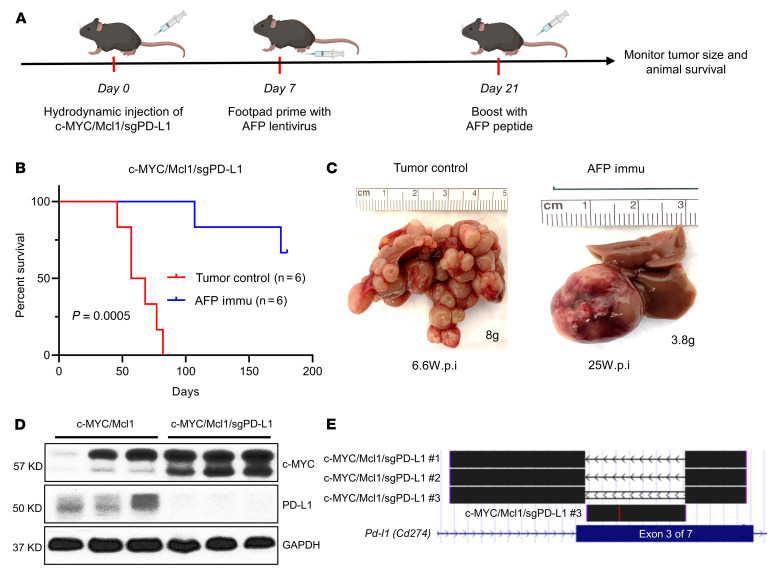
Figure 7. Deletion of PD-L1 does not affect tumor growth.
(A) Study design. (B) Survival curve of c-MYC/Mcl1/sgPD-L1 with or without AFP immunization. Kaplan-Meier test was used for survival analysis. (C) Pictures of representative livers from B, the numbers indicate the liver weight and weeks from hydrodynamic injection to sacrifice date for that particular mouse. (D and E) Western blot (D) and TA cloning sequencing results (E) from the c-MYC/Mcl1/sgPD-L1 tumors also confirm the deletion of PD-L1 in the tumors. The TA cloning sequencing reads are aligned with mouse GRCm38/mm10 genome at the UCSC genome browser (https://genome.ucsc.edu/). PD-L1 is also called CD274, and the gRNAs are designed to target the third exon of Pd-l1. c-MYC/Mcl1/sgPD-L1 no. 1 and c-MYC/Mcl1/sgPD-L1 no. 2 indicate the depletion of the whole sequence between the 2 sgPD-L1 gRNAs, c-MYC/Mcl1/sgPD-L1 no. 3 indicate the reversion sequence between the 2 sgPD-L1 gRNAs. All these sequence edits cause PD-L1 gene sequence frame-shift and early stop. wpi, weeks after injection; Immu, immunization.