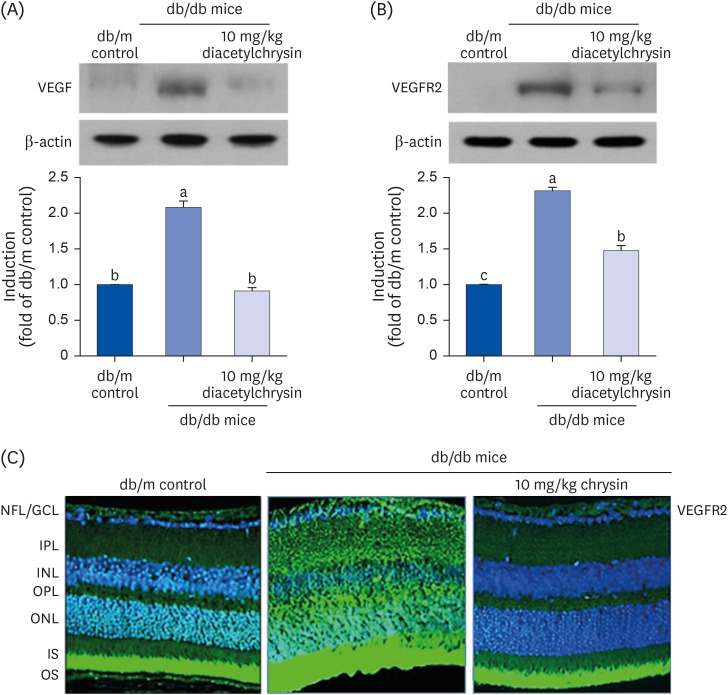
Fig. 7. Inhibition of retinal tissue induction of VEGF (A) and VEGFR2 (B) by diacetylchrysin. The db/db mice were orally administered 10 mg/kg diacetylchrysin daily for 10 weeks. The db/m mice were employed as control animals. Mouse retinal tissue extracts were subject to Western blot analysis with a primary antibody against VEGF and VEGFR2 (A and B, respectively). β-Actin protein was used as an internal control. Bar graphs (mean ± SEM, n = 3) in the right panel represent densitometric results of left blot bands. Values not sharing a common small letter differ, P < 0.05. Immunocytochemical analysis of VEGFR2 in db/db mice treated with 10 mg/kg chrysin was achieved by histological staining of mouse retina sections using a primary antibody of VEGFR2. FITC-conjugated secondary antibody was used for visualizing the VEGFR2, and the nuclear staining was done with 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (C). Each photograph is representative of 4 mice. Magnification: 200-fold. Retinal layers are labeled as follows: NFL/GCL, IPL, INL, OPL, ONL, and photoreceptor IS/OS.
VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor; VEGFR2, VEGF receptor 2; SEM, standard error of mean; FITC, fluorescein isothiocyanate; NFL, neurofiber layer; GCL, ganglion cell layer; IPL, inner plexiform layer; INL, inner nuclear layer; OPL, outer plexiform layer; ONL, outer nuclear layer; IS, inner segment; OS, outer segment.