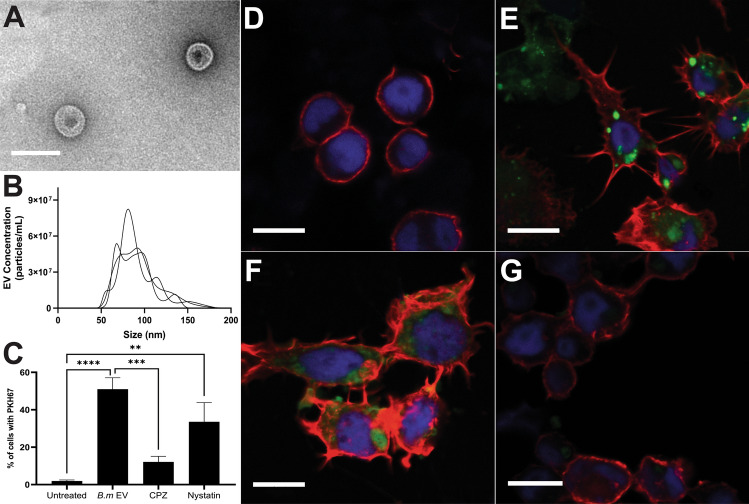
Figure 1.
B. malayi mf derived EVs are internalized by Aag2 cells. Isolation of B. malayi mf EVs was confirmed by TEM (A) and size and concentration profile further validated with nanoparticle tracking analysis (B). In this representative graph, each line trace indicates a biological replicate EV sample isolated from discrete mf cultures. PKH67-stained B. malayi mf EVs were incubated with Aag2 cells for 24 h and EV internalization quantified using a BD Accuri C6 Flow Cytometer (C) with 51% of Aag2 cells internalizing B. malayi mf EVs. The endocytosis inhibitors chlorpromazine (CPZ) and nystatin were used to determine the mechanism by which these EVs are being internalized. CPZ significantly reduced EV internalization by 39% while nystatin did not. Additionally, EV internalization was assessed by confocal microscopy using a Leica SP5 X MP confocal/multiphoton microscope system. Aag2 cells were labeled with AlexaFluor 647 Phalloidin (red) and DAPI (blue) to visualize nuclei. Aag2 cells internalized PKH67-stained B. malayi mf EVs (green) (E) as compared to control cells (D). Cells treated with CPZ (G) showed reduced endocytosis of stained EVs while cells treated with nystatin (F) showed continued uptake of EVs. N = 3 experiments (minimum). Mean ± SEM. **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001. Scale bar (A) = 150 nm. Scale bar (D-G) = 10 µM.