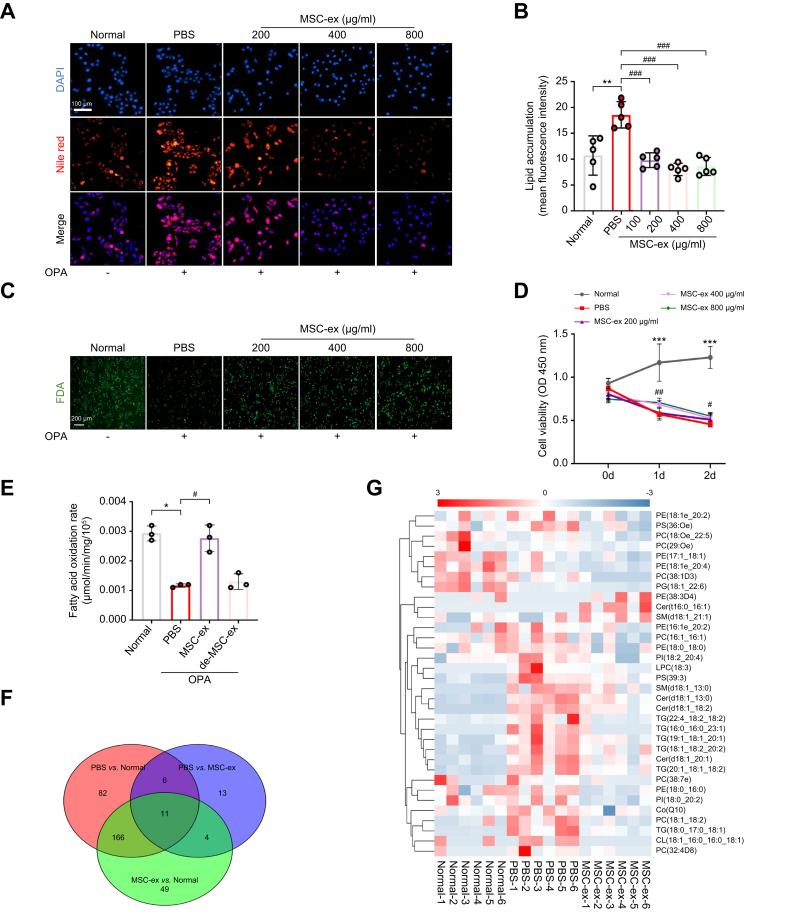
Fig. 2.
MSC-ex inhibit lipid accumulation in vitro by promoting the β-oxidation of fatty acids and suppressing the fatty acid synthesis.
(A and B) Intracellular lipid droplets in L02 cells stimulated with OPA (2.0 mM, 2:1 ratio) in combination with different concentrations of MSC-ex or PBS for 24 h were visualised by Nile red staining (A) and quantified by ImageJ for five random areas (B). Scale bars, 100 μm. (C) Cell viability was measured by FDA staining. (D) The effect of MSC-ex on the viability of L02 cells was determined by CCK-8 assay. (E) Mitochondrial fatty acid β-oxidation of L02 cells treated with a combination of OPA and MSC-ex (800 μg/ml) or deMSC-ex for 24 h, n = 3 biological replicates per group. (F and G) Lipogenic metabolites in L02 cells subjected to stimulation with OPA (2.0 mM, 2:1 ratio) combined with MSC-ex (800 μg/ml) or PBS treatment for 24 h were observed by non-targeted lipidomics (n = 6 per group), followed by Venn diagram (F) and heat map (G) analyses of fatty acid metabolites. Data are represented as mean ± SEM. Statistical analyses by a one-way ANOVA (B, D, and E). ∗p <0.05, ∗∗p <0.01, ∗∗∗p <0.001 vs. normal group; #p <0.05, ##p <0.01, ###p <0.001 vs. PBS group. CCK-8, Cell Counting Kit-8; deMSC-ex, MSC-ex-free conditional medium supernatant; FDA, fluorescein diacetate; MSC-ex, MSC-derived exosomes; MSC, mesenchymal stem cell; OPA, oleate and palmitate.