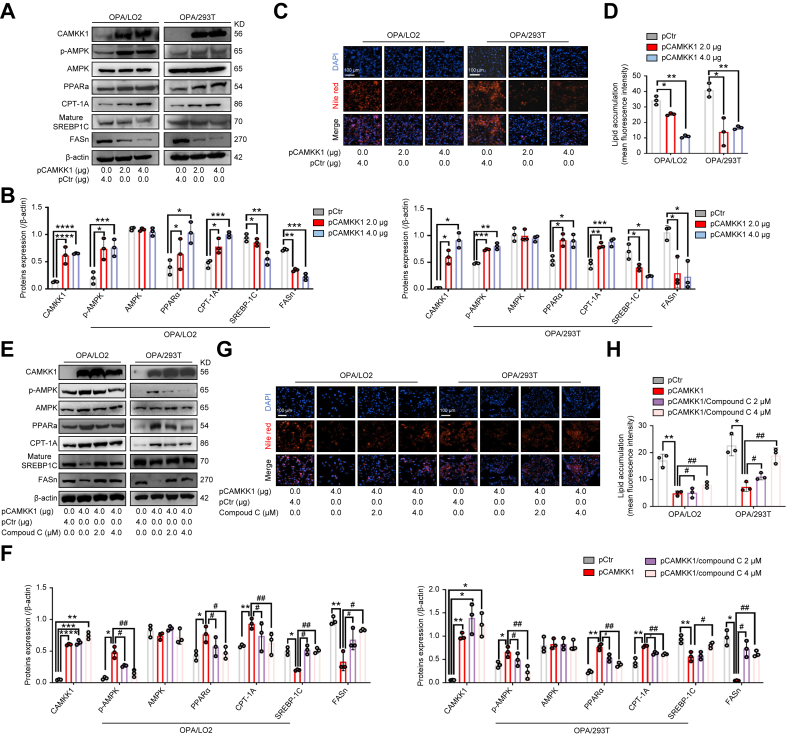
Fig. 5.
Overexpression of CAMKK1 activates the AMPK signalling pathway and attenuates lipid accumulation in OPA-treated L02 and 293T cells.
(A and B) The expression of AMPK signalling proteins in L02 and 293T cells transfected with pCAMKK1 (2 and 4 μg) or pCtr control vector before OPA stimulation (2.0 mM, 2:1 ratio) for 24 h was detected by immunoblotting (A) and quantified (B). (C and D) Intracellular lipid droplets in L02 and 293T cells were visualised by Nile red staining (C) and quantified by ImageJ for five random areas (D). Scale bars, 100 μm. (E and F) The expression of AMPK signalling proteins in L02 and 293T cells after transfection with pCAMKK1 (4 μg) or pCtr vector and OPA stimulation (2.0 mM, 2:1 ratio) with or without compound C (2 and 4 μM) treatment for 24 h was examined by immunoblotting (E) and quantified (F). (G and H) Intracellular lipid accumulation was visualised by Nile red staining (G) and quantified by ImageJ for three random areas (H). Data are represented as the mean ± SEM. Statistical analyses by unpaired two-tailed Student’s t test (B and D) and a one-way ANOVA (F and H). ∗p <0.05, ∗∗p <0.01, ∗∗∗p <0.001, ∗∗∗∗p <0.0001 vs. pCtr group; #p <0.05, ##p <0.01 vs. pCAMKK1 (4 μg) group. AMPK, AMP-activated protein kinase; CAMKK1, calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase 1; CPT-1A, carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1A; FASn, fatty acid synthase; OPA, oleate and palmitate; p-AMPK, phosphorylated AMPK; PPARα, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha; SREBP-1C, sterol regulatory element-binding protein-1C.