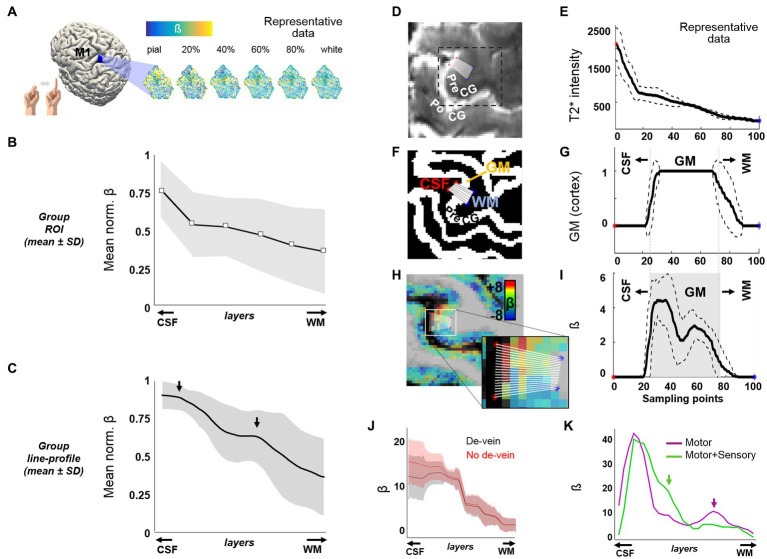
Figure 1.
Cortical depth-dependent motor task-evoked BOLD fMRI. (A) Flattened patches of M1 extracted from six surfaces at different cortical depths in one volunteer. (B) The plot shows the mean ± SD of the normalized beta-coefficient in six cortical patches of M1 at different cortical depths (N = 13). (C) Mean ± SD of the normalized activation line-profiles, computed from the beta map of 13 subjects, using a line-profile method on a particular segment of M1 computation explained through panels (D–I). The arrows point to the two main activation peaks observed along the cortical depth. (D) The figure shows part of a mean TR-external EPIK axial slice containing the precentral gyrus (PreCG). The 20 overlaid sampling lines (in white) extend from the CSF, covering the cortical thickness, up to the WM. (E) Average line profile of the mean TR-external EPIK on the selected sampling region. Note the high intensity at the initial points (CSF, with long T2 constant). The dashed lines above and below the solid line represent the mean ± SD. (F) Same region as in (D), cropped from the segmented MP2RAGE, which identifies the cortical ribbon (in white color, labeled as GM). (G) Line profile calculated from the sampling lines over the image in (F). (H) Beta coefficient map overlaid on the MP2RAGE and zoomed view of the 20 sampling lines. (I) Profile of the beta coefficient along the selected lines crossing the finger motor area in the PreCG. Note the higher signal on superficial and middle layers of the cerebral cortex (double peak, typical of motor tasks). The gray-shaded area in (I) represents the extent of the GM, with superficial layers (near the CSF) on the left and deep layers (near the WM), on the right. (J) An example of an evoked line profile computed before (red) and after (black) the addition of the de-vein correction step. (K) Line profiles in a subject performing either finger movement only (purple trace) or finger movement involving touch (green trace). In panels (E, G, I, K), the x-axis refers to the distance from the CSF to the WM, equidistantly sampled with 100 points.