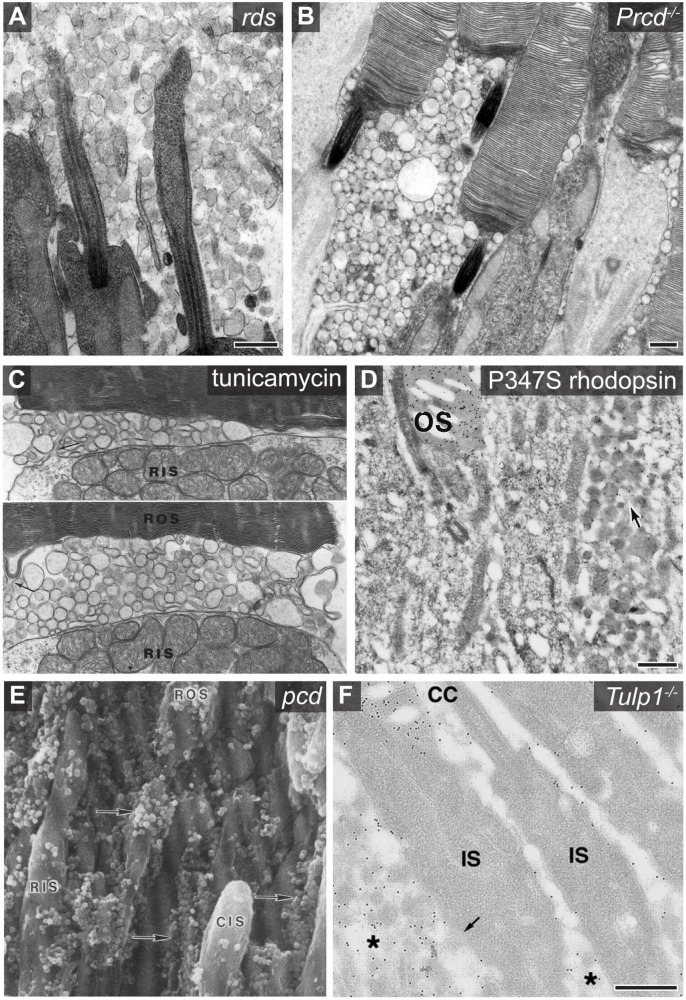
FIGURE 2.
Examples of photoreceptor derived extracellular vesicle accumulation associated with retinal pathology. (A) An electron micrograph showing the accumulation of photoreceptor derived ciliary ectosomes in the subretinal space of rds mice. Scale bar is 500 nm. Image used with permission of Rockefeller University Press, from Salinas et al. (2017); permission conveyed through Copyright Clearance Center, Inc. (B) An electron micrograph showing the accumulation of ectosomes between photoreceptor cells of Prcd–/– mice. Scale bar is 500 nm. Image adapted from Spencer et al. (2019a). Copyright 2019 National Academy of Sciences. (C) Two electron micrographs centered at the base of Xenopus photoreceptor outer segments showing the accumulation of vesicles between the rod inner segment (RIS) and rod outer segment (ROS) after a 6 h incubation of the retina with tunicamycin. Protrusions of the inner segment plasma membrane (arrow in top image) and most basal disc membrane (arrow in bottom image) indicate possible sites of origin for the vesicles. Image adapted from Wetzel et al. (1993). (D) An electron micrograph of an anti-rhodopsin immunogold labeled retinal cross section obtained from a transgenic mouse expressing P347S rhodopsin. The arrow denotes the accumulation of rhodopsin containing extracellular vesicles between photoreceptor cells. Scale bar is 500 nm. The outer segment (OS) is labeled. Image adapted from Li et al. (1996). Copyright 1996 National Academy of Sciences. (E) A scanning electron micrograph of a pcd mouse retinal cross section which shows the accumulation of extracellular vesicles adjacent to photoreceptor inner and outer segments. The vesicles, highlighted with arrows, were originally described as spherical excrescences or spherules based on their appearance. Image reprinted from Blanks et al. (1982), with permission from Elsevier. (F) An electron micrograph of an anti-rhodopsin immunogold labeled retinal cross section obtained from a Tulp1–/– mouse retina. The asterisk labels extracellular vesicles which are enriched with rhodopsin. The outer segment (OS), connecting cilium (CC), and inner segment (IS) are labeled. Scale bar is 500 nm. Image used with permission from Association for Research in Vision and Ophthalmology, from Hagstrom et al. (2001); permission conveyed through Copyright Clearance Center, Inc.