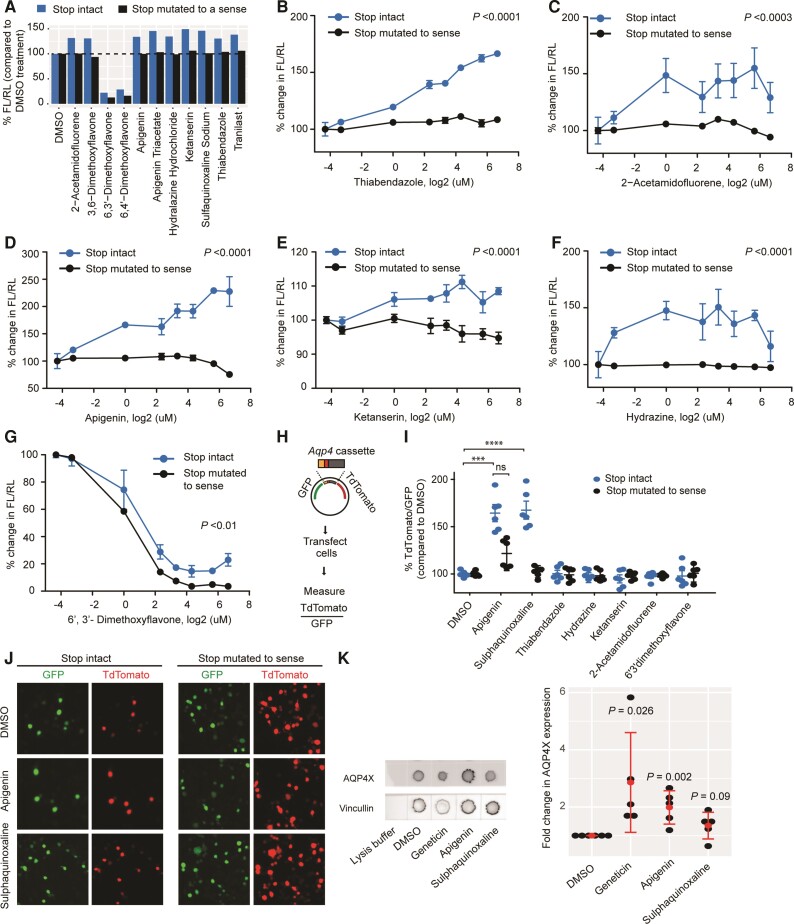
Figure 3.
Validation of candidate compounds. (A) Retesting with dual-luciferase vectors in which the Aqp4 stop codon is either intact (blue) or mutated to a sense codon (black). Compounds altering readthrough by at least 30% are shown. Enhancers cease activity in the absence of stop codon. (B–G) Dose-response curves for candidate compounds. Concentrations are log2-transformed. For log transformation of 0 µM (DMSO alone), a value of 0.05 µM was used. Enhancers cease to be active (B–F), whereas an inhibitor continues to be active (G) in the absence of stop codon. n = 3. ANOVA followed by a post hoc Tukey was used to compare the means for the two constructs across concentrations. (H) Dual-fluorescence assay. Readthrough is measured as TdTomato/GFP (I) dual-fluorescence assays in which the Aqp4 stop codon is either intact (blue) or mutated to a sense codon (black). ****P ≤ 0.0001; ***P ≤ 0.001, n = 3, t-test. (J) Representative images for dual-fluorescence assay with apigenin and sulphaquinoxaline. (K) Dot blot demonstrates apigenin enhances readthrough of endogenous Aqp4 transcript in cultured astrocytes. AQP4X expression is normalized to Vincullin. Red dots represent means and bars represents standard deviations. t-test comparing DMSO and compounds. n = 3 **P ≤ 0.01; *P ≤ 0.05.