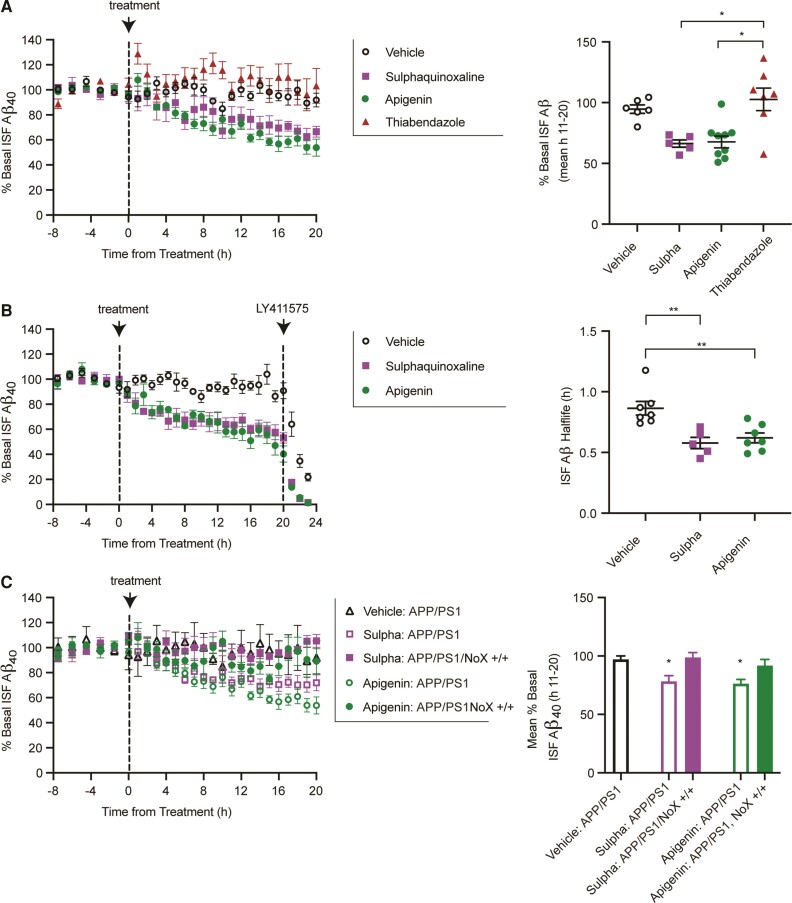
Figure 4.
Compounds lower Aβ in a readthrough dependent manner. (A) Continuous reverse microdialysis administration of sulphaquinoxaline (200 μM) and apigenin (100 μM) reduces hippocampal ISF Aβ in APP/PS1 mice over a 20 h period, while a non-readthrough promoting compound, thiabendazole (400 μM), does not (left). Concentrations vary based on in vitro potency. Sulphaquinoxaline and apigenin reduce ISF Aβ by 29.9 ± 3.2 and 27.3 ± 5.2%, respectively, compared to vehicle-treated mice (n = 6) (right). In contrast, thiabendazole was not significantly different from vehicle, but significantly higher than the other treatment groups (mean over hours 11–20 of administration; Kruskal–Wallis test). (B) A separate cohort of APP/PS1 mice was treated with apigenin, sulphaquinoxaline or vehicle by reverse microdialysis for 20 h following by LY411575 (3 mg/kg intraperitoneally). The ISF Aβ elimination half-lives in apigenin and sulphaquinoxaline treated mice were 0.62 ± 0.04 and 0.57 ± 0.47 h, respectively, compared to vehicle-treated mice at 0.86 ± 0.56 h. (C) Sulphaquinoxaline and apigenin do not alter interstitial Aβ in APP/PS1 mice deficient in Aqp4 readthrough. Data presented as mean ± SEM. See Supplementary Table 1 for n and statistical tests. *P = 0.01, **P = 0.001.