Fig. 1.
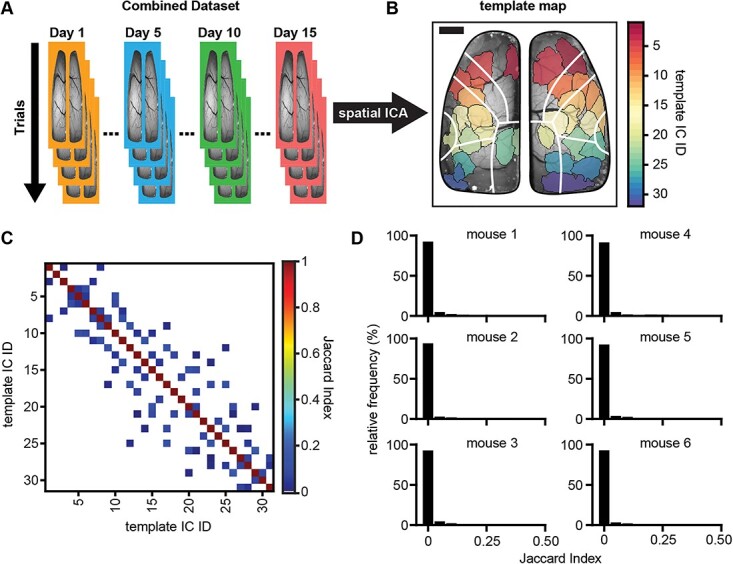
Spatial ICA of wide-field Ca2+ imaging data produces spatially independent brain regions. A) Schematic showing the ICA workflow of concatenating data for each animal chronologically across days and trials (days are signified by different colored borders; trials are signified by overlapping images) and sending the combined dataset through the JADE ICA algorithm. B) Example template map (ground-truth to which all other ICA solutions are compared) of spatial ICs produced from running ICA on one mouse’s combined dataset (each different colored region is a single IC; scale bar: 1 mm). White lines denote major regions of the Allen Common Coordinate Framework (CCF; see Supplementary Fig. S2). C) Example matrix of Jaccard indices comparing the template map to itself (low off-diagonal Jaccard indices indicate good spatial separation; zero values are shown as white indicating no IC overlap). D) Frequency histograms showing the distribution of off-diagonal Jaccard indices (nonself matches) when comparing the template map to itself for each animal (bin-widths = 0.05).
