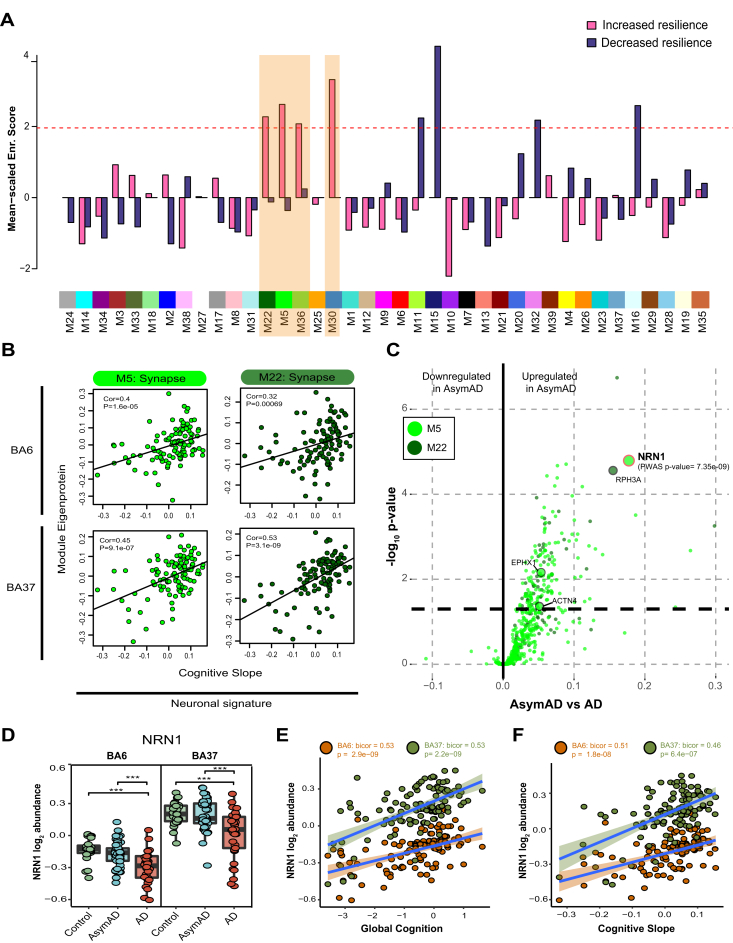
Fig. 3.
Integrated proteomics of human brain reveals NRN1 as a top resilience candidate.A, significant enrichment of modules associated with increased cognitive resilience was identified by PWAS in consensus modules. The dashed red line illustrates the significance cutoff corresponding to a Z score of 1.96 or p = 0.05. Significant, increased resilience modules are highlighted in orange. B, PWAS significant, synaptic modules M5 and M22 positively correlate with cognitive slope, irrespective of the brain region. Bicor and p values (BA6: M22 cor = 0.32, M22 p = 0.00069, M5 cor = 0.4, M5 p = 1.6e-05; BA37: M22 cor = 0.53, M22 p = 3.1e-09, M5 cor = 0.45, M5 p = 9.1e-07). C, differential expression comparing AsymAD and AD groups from M5 and M22 module members. Protein fold-change is the x-coordinate and the −log10p value from one-way ANOVA is the y coordinate for each protein. Proteins above the dashed line (p = 0.05) are considered significantly differentially expressed. Large circles highlight proteins that were significant by PWAS (α = 5e-06). D, NRN1 abundance is significantly reduced in AD. One-way ANOVA (BA6: F = 13.25, p < 0.001; BA37: F = 13.68, p < 0.001) with Tukey test. E, NRN1 abundance correlates positively with global cognitive performance. Bicor and p values (BA6: bicor = 0.53, p = 2.9e-09; BA37: bicor = 0.53, p = 2.2e-09). F, NRN1 abundance correlates positively with cognitive slope. Bicor and p values (BA6: bicor = 0.51, p = 1.8e-08; BA37: bicor = 0.46, p = 6.4e-07). AD, Alzheimer’s disease; AysmAD, asymptomatic AD; BA6, Brodmann area 6; BA37, Brodmann area 37; NRN1, neuritin; PWAS, proteome-wide association study.