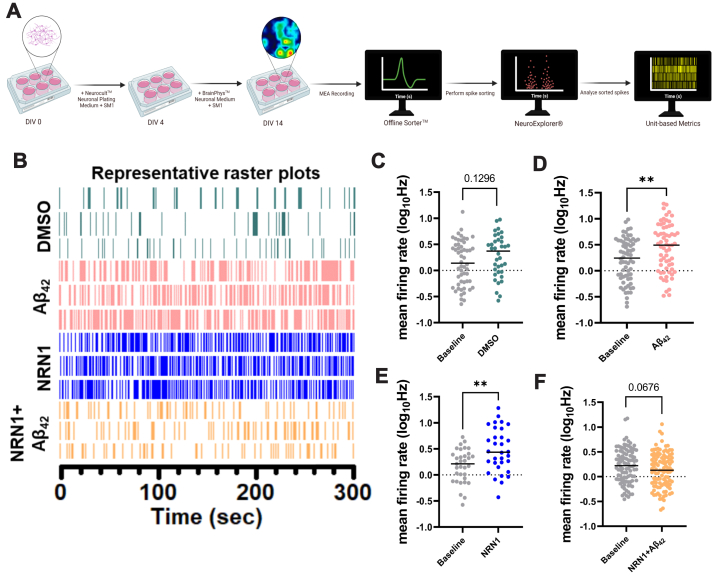
Fig. 5.
NRN1 protects against Aβ42-induced neuronal hyperexcitability.A, schematic representation of primary rat hippocampal neuron treatment and single neuron electrophysiology analysis. B, representative raster plots from three units after exposure to DMSO, 500 nM Aβ42, 150 ng/ml NRN1, or 150 ng/ml NRN1 and 500 nM Aβ42. C, mean firing rate at DIV14 in hippocampal neurons treated with DMSO, compared to baseline (n = 36–54 neurons, unpaired Student’s t test; p = 0.1296). D, mean firing rate at DIV14 in hippocampal neurons treated with 500 nM Aβ42, compared to baseline (n = 65–68 neurons, unpaired Student’s t test; p = 0.0022). E, mean firing rate at DIV14 in hippocampal neurons treated with 150 ng/ml NRN1, compared to baseline (n = 32–33 neurons, unpaired Student’s t test; p = 0.0023). F, mean firing rate at DIV14 in hippocampal neurons treated with 150 ng/ml NRN1 and 500 nM Aβ42, compared to baseline (n = 100–107 neurons, unpaired Student’s t test; p = 0.0676). Aβ, amyloid-beta; NRN1, neuritin.