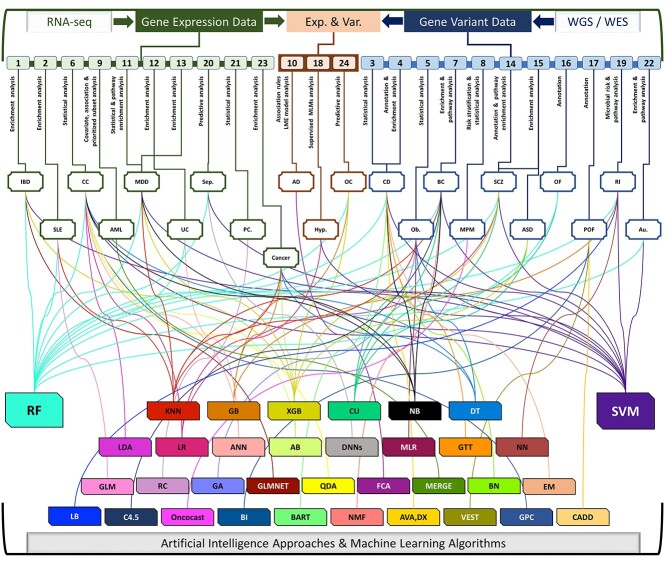
Figure 1.
AI/ML approaches using gene variant and gene expression data for traditional bioinformatics and predictive analysis. Figure includes 24 AI/ML approaches, variable diseases [inflammatory bowel disease (IBD); systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE); colon cancer (CC); acute myeloid leukemia (AML); major depressive disorder (MDD); ulcerative colitis (UC); sepsis (Sep.); prostate cancer (PC.); Alzheimer’s disease (AD); hypertension (Hyp.); ovarian cancer (OC); Crohn’s disease (CD); obesity (Ob.); breast cancer (BC); malignant pleural mesothelioma (MPM); schizophrenia (SCZ); autism spectrum disorder (ASD); ovarian failure (OF); premature ovarian failure (POF); risk of illness (RI); autism (Au.)] and AI/ML algorithms [Generalized linear models (GLM); Genetic Algorithm (GA); Multivariate Linear Regression (MLR); Random Forest (RF); Bayesian Networks (BN); Support Vector Machine(SVM); Expectation–Maximization (EM); Bioinformatics Analysis (BI); Random committee ensemble learning (RC); Elastic net regularized generalized linear model (GLMNET); Linear discriminant analysis (LDA); Quadratic Discriminant Analysis (QDA); AdaBoost(AB); Formal Concept Analysis (FCA); Combined Annotation Dependent Depletion (CADD); Very Efficient Substitution Transposition (VEST); Deep Learning Neural Networks (DNNs); Decision Tree (DT); LogitBoost (LB); Gradient boosting (GB); Extreme gradient boosting (XGB); Gaussian Process Classification (GPC); Logistic Regression (LR); Artificial Neural Network (ANN); Greedy Thick Thinning algorithm (GTT); Neural Networks(NN); K-Nearest Neighbors (K-NN); Clustering (CU); Non-negative Matrix Factorization (NMF); Naïve Bayes (NB); MERGE (mutation, expression hubs, known regulators, genomic CNV and methylation); Bayesian Additive Regression Trees (BART)].