Figure 2.
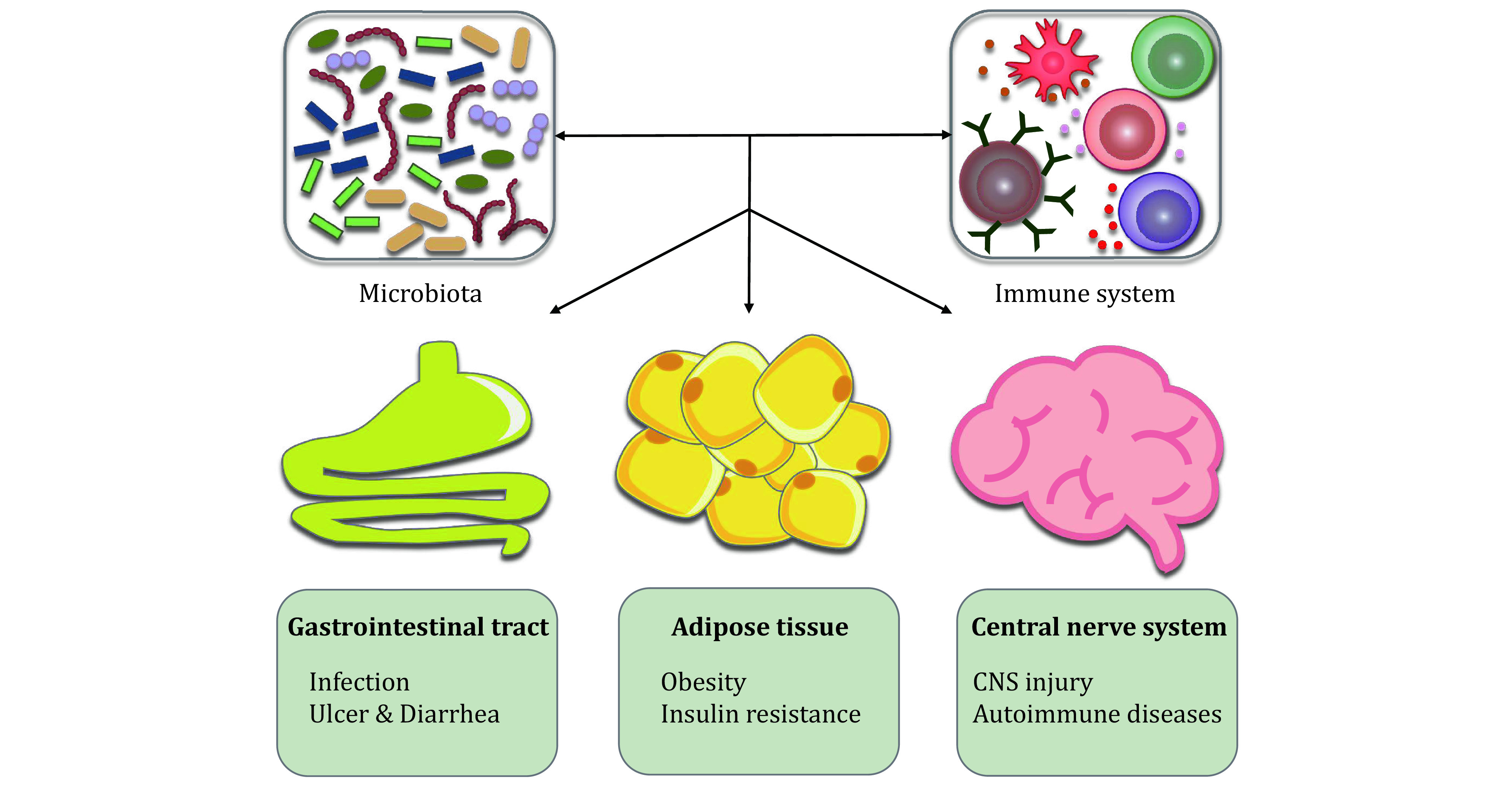
The host-microbiota interaction in diseases. Microbiota and their metabolites regulate the development and function of the immune system, and thus influence diseases in multiple tissues. In the gastrointestinal tract, the microbiota dysbiosis causes infectious diseases, and the host shows symptoms of ulcer and diarrhea. In the adipose tissue, the microbiota contributes to metabolic diseases, such as obesity and insulin resistance. In the central nerve system, the microbiota involves in the incidence and recovery of CNS injury and autoimmune diseases
