Figure 3.
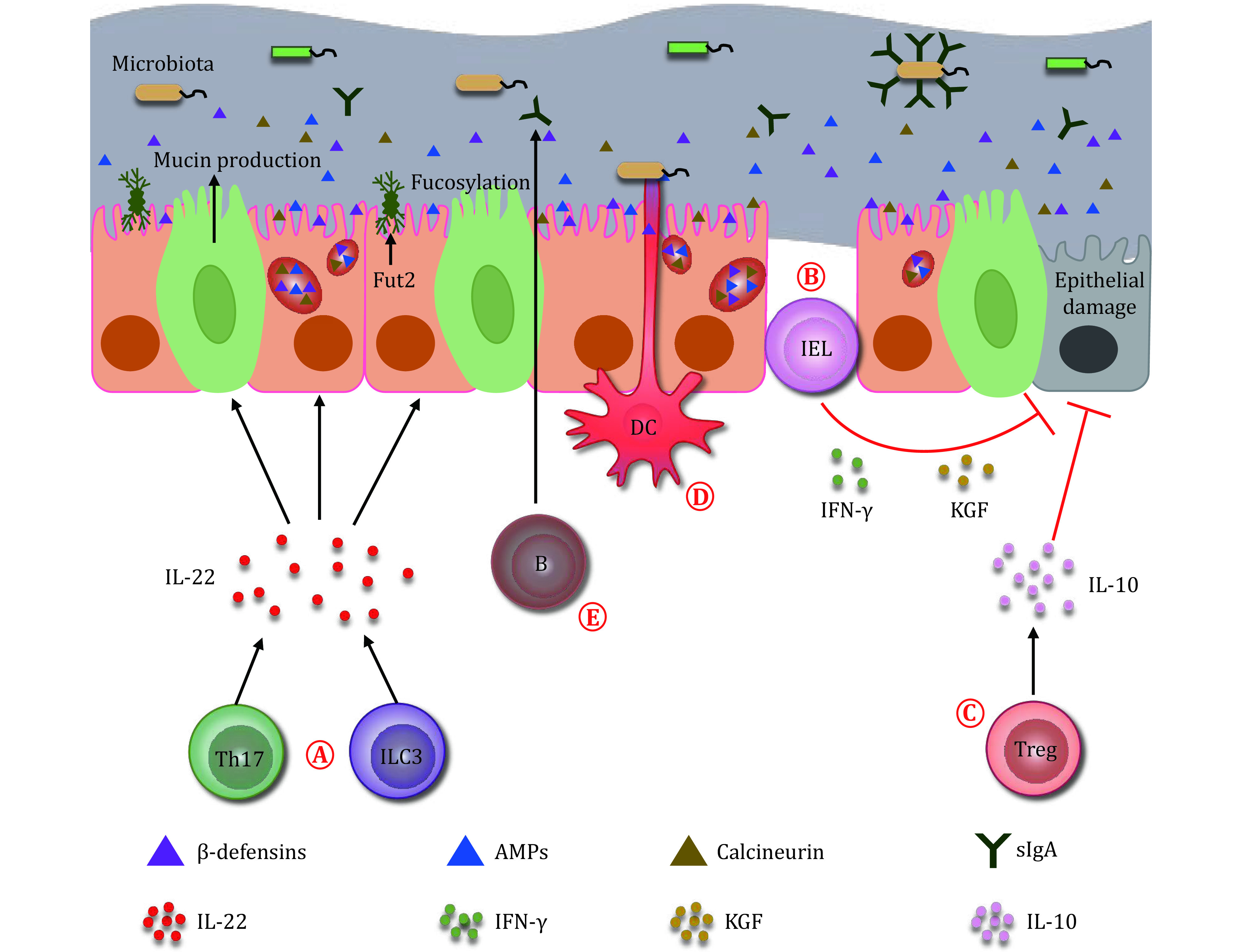
Immune system regulates the microbiota. A Microbiota is regulated by ILC3 and Th17 cells. The ILC3 and Th17 cells inhibit the growth of microbiota through producing IL-22 and inducing epithelial cells to secrete β-defensins, antimicrobial peptides and calcineurin. The IL-22 also induces epithelial cells to secrete mucin, and thus represses the transmission of gut bacteria. In addition, the IL-22 upregulates Fut2 expression in the epithelial cells, and increases the fucosylation on their surface, which benefits the proliferation of commensals in the gut. B IELs protect the damage of epithelial cells through producing cytokines such as IFN-γ and keratinocyte growth factors (KGF). C Treg cells repress the damage of epithelium by secreting IL-10. D DCs protrude their synapses through the intestinal epithelium to the gut lumen to sense the microbiota. E B cells produce secretory IgA (sIgA) to the gut lumen. The sIgA coats on the colitogenic bacteria to help with their clearance
