Figure 1.
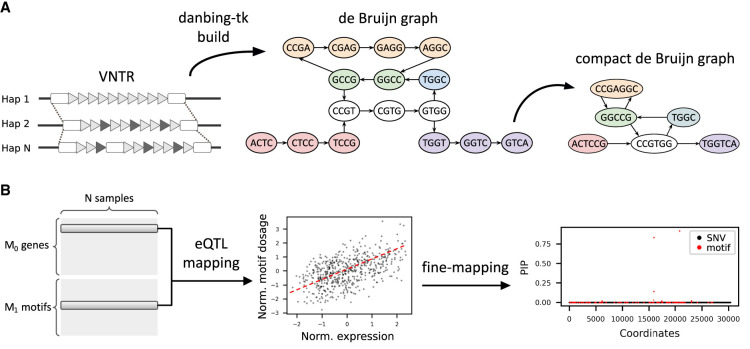
Methods overview. (A) Estimating the dosages of VNTR motifs using a locus-RPGG. A locus-RPGG is built from haplotype-resolved assemblies by first annotating the orthology mapping of VNTR boundaries and then encoding the VNTR alleles with a de Bruijn graph (dBG), or locus-RPGG. A compact dBG is constructed by merging nodes on a nonbranching path into a unitig, denoted as a motif in this context. Motif dosages of a VNTR can be computed by aligning short reads to an RPGG and averaging the coverage of nodes corresponding to the same motif. (B) Identifying likely causal eMotifs. The dosage of each motif is tested against the expression level of a nearby gene. Genes in significant association with at least one motif (denoted as eMotif) are fine-mapped using susieR (Wang et al. 2020) in order to identify eMotifs that are likely causal to nearby gene expression. All GTEx variants and lead motifs from each gene–VNTR pair are included in the fine-mapping model.