FIGURE 3.
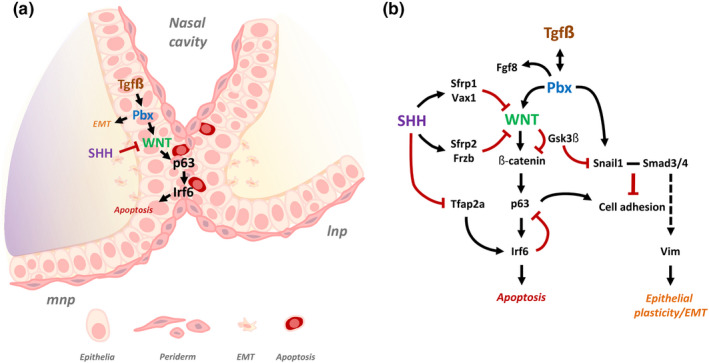
Molecular mechanisms of lip fusion and epithelial seam dissolution. (a) Schematic diagram of the lambdoidal (λ) epithelial seam at E11.5, formed through fusion of the medial nasal and lateral nasal processes. SHH and TGFβ‐mediated Pbx signalling converge on WNT to regulate pathways involved in epithelial seam dissolution. (b) Pbx plays a dual‐role in lip fusion, (1) by regulating a WNT‐p63‐Irf6 cascade to promote epithelial apoptosis; (2) by promoting epithelial‐mesenchymal transformation, cell plasticity/migration through regulation of Snail1. Cross‐talk between both pathways is achieved by post‐translational modification of Gsk3β on Snail1. SHH ensures appropriate p63‐Irf6 signalling by up‐regulating WNT antagonists and restricting Tfap2a signalling. (Adapted from Kurosaka et al., 2014; Losa et al., 2018). mnp, medial nasal process; lnp, lateral nasal process; EMT, epithelial‐mesenchymal transformation
