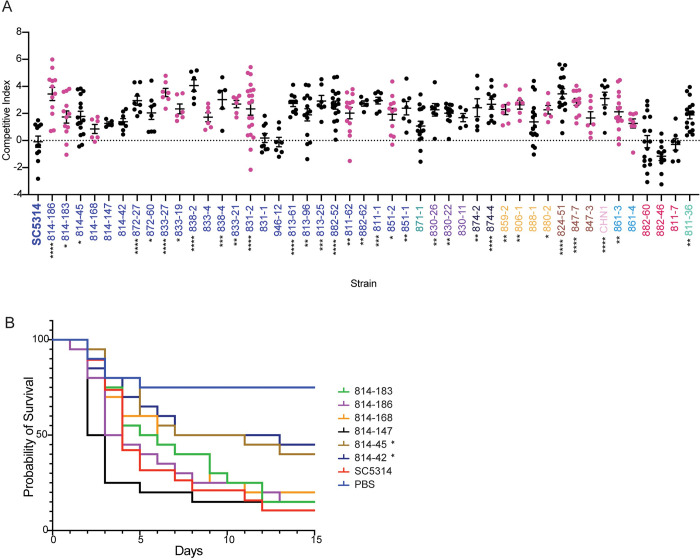
Fig 6. Commensal isolates retain pathogenic potential.
(A) Competition assays in G. mellonella demonstrate increased fitness of many commensal isolates compared to SC5314 reference. Isolates were competed against a fluorescent SC5314 isolate, starting at a 1:1 initial inoculum. Competitive fitness was calculated as the ratio between fluorescent and nonfluorescent colonies, normalized to the inoculum, and log2 transformed. Black data points indicate an oral isolate and pink data points indicate a fecal isolate. Significant differences from the SC5314 reference strain were determined by one-way ANOVA, with Dunnett’s multiple correction testing. (B) Survival assays in G. mellonella, comparing the SC5314 reference to 6 isolates from donor 814. Each strain was standardized to 2 × 106 cells/mL before inoculating 20 G. mellonella larvae per strain with 50 μL of prepared inoculum. Larvae were monitored daily for survival. Statistical differences were determined using a Mantel–Cox log-rank test. Asterisks indicate P < 0.05 (*), P < 0.005 (**), P < 0.001 (***), and P < 0.0001 (****) compared with SC5314.