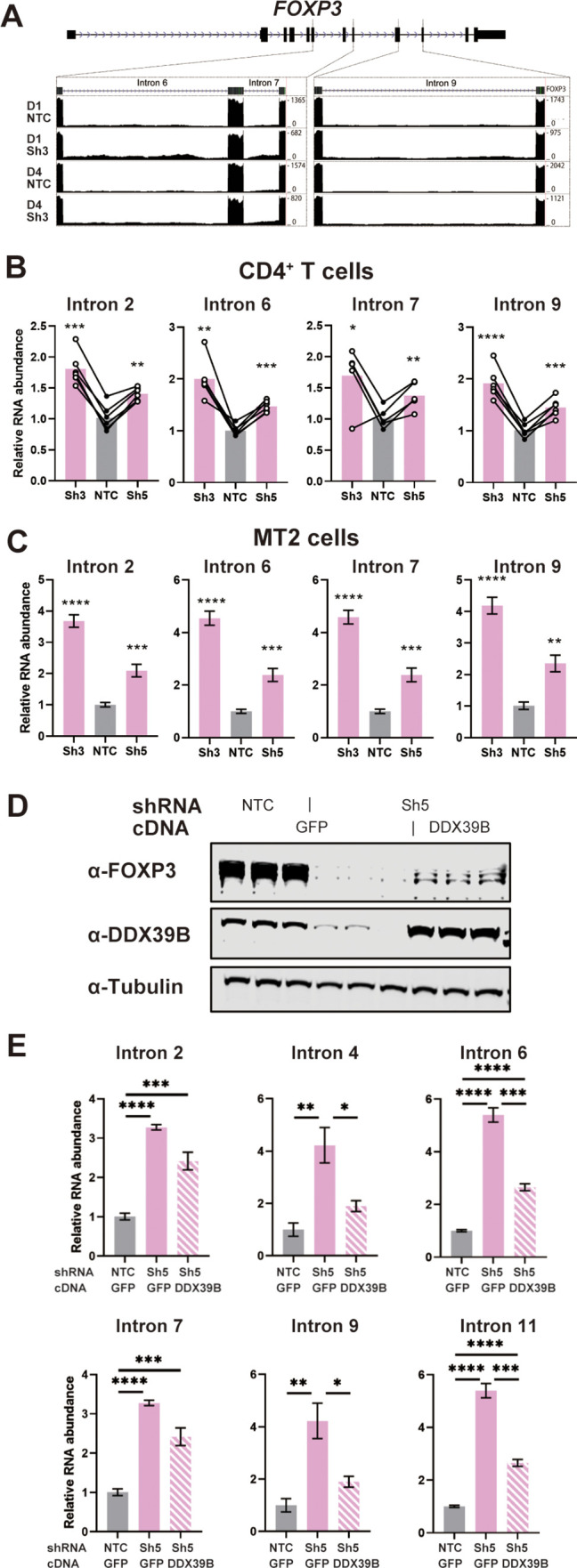
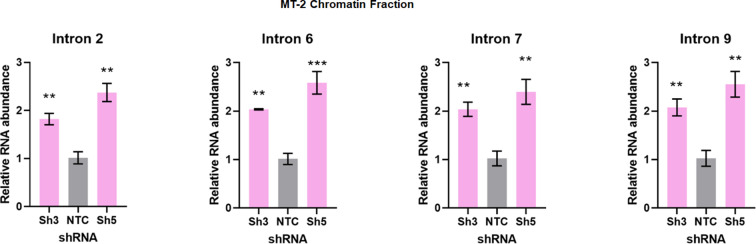
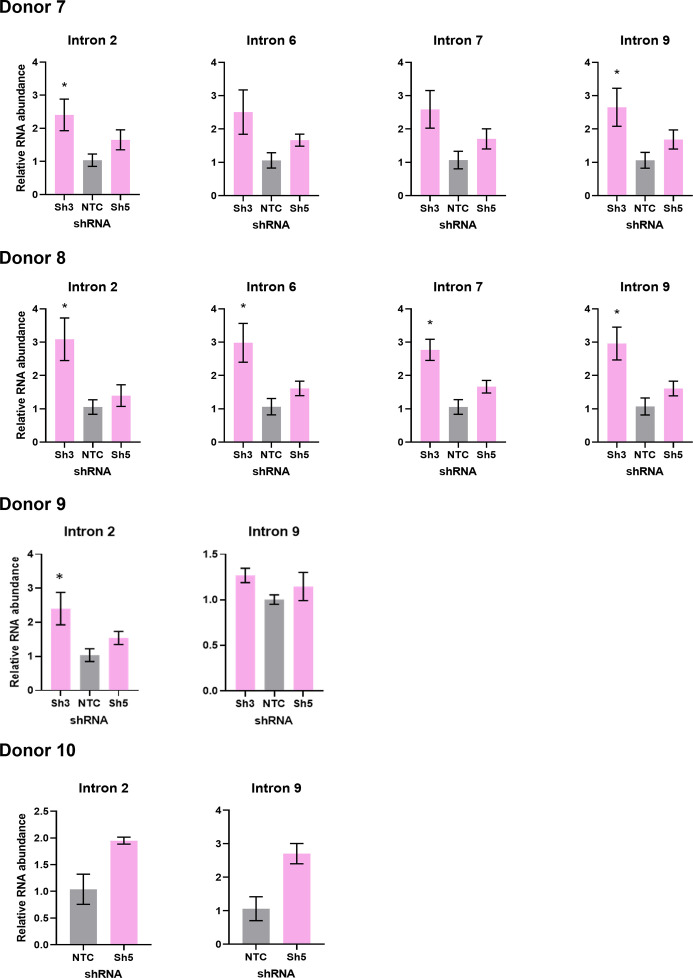
Figure 5. DDX39B depletion triggers the retention of FOXP3 introns.
(A) RNAseq reads mapping to the FOXP3 genomic region in control (NTC) or DDX39B depleted (Sh3) CD4+ T cells from Donors 1 and 4. Read counts for FOXP3 introns 6, 7, and 9 are shown on the Y-axis in the two insets. (B, C) Abundance of FOXP3 RNA introns relative to total FOXP3 RNA after DDX39B depletion in CD4+ T cells from six donors (B) or MT-2 cells (C). (D–E) Rescue of the DDX39B depletion (Sh3) by exogenous expression (GFP or DDX39B) in MT-2 cells. The abundance of FOXP3 and DDX39B relative to Tubulin (D) or FOXP3 RNA introns relative to total FOXP3 RNA (E) are shown.*: p<0.05, **: p<0.01, ***: p<0.001 and ****: p<0.0001.