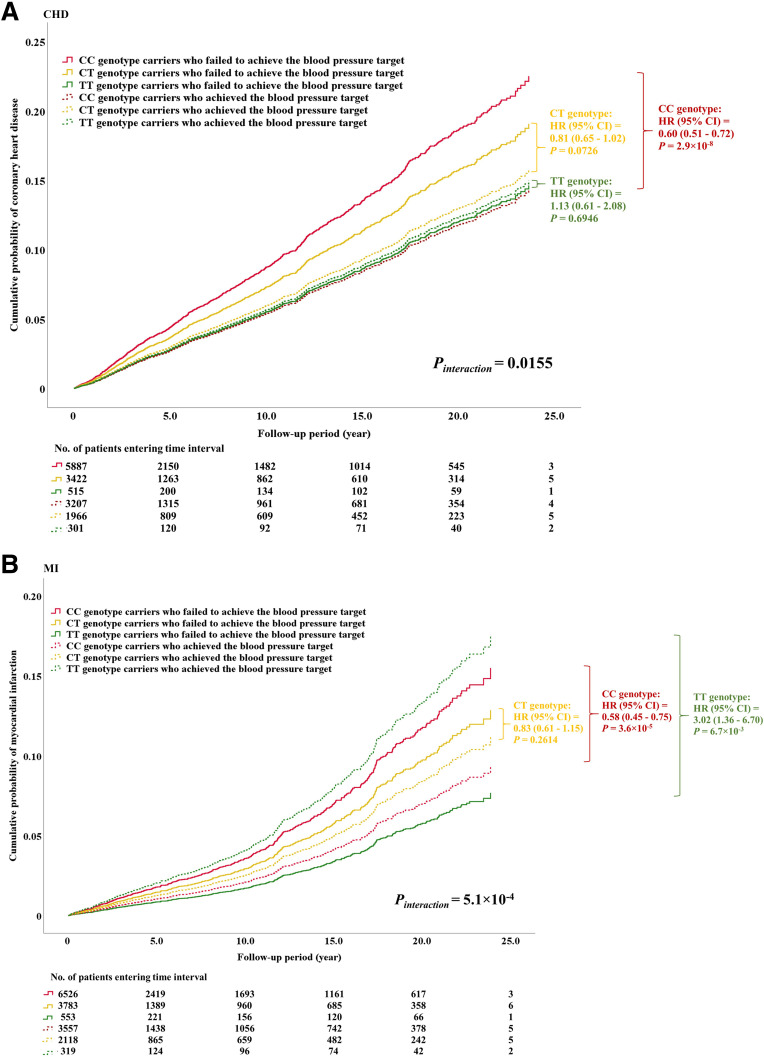
Figure 3.
Modulating influence of PDE1A rs10171703 on the association between BP control and new-onset cardiovascular complications among Chinese patients with T2D. These analyses were conducted in the combined cohort of the HKDR study and the HKDB phase 1 and 2 studies. Cumulative probability of new-onset CHD (A) and MI (B) is shown according to the combinations of PDE1A rs10171703 genotypes and the status of BP control. Pinteraction was the P value of the interaction term obtained from the Cox regression model including two main effects (PDE1A rs10171703 and achievement of BP target [i.e., SBP <130 mmHg and DBP <80 mmHg]), the interaction term of main effects, and the covariates (the study cohorts [HKDR study, HKDB phase 1 and 2 studies], enrollment year, sex, age, duration of diabetes, and principal components). P values and HRs and 95% CIs were obtained from the Cox regression model assessing the association between the achievement of BP target (“yes” [coded as 1] vs. “no” [coded as 0]) and diabetic cardiovascular complications, with adjustment for study cohorts, enrollment year, sex, age, duration of diabetes, and PCs, stratified by the genotypes of rs10171703. Numbers of patients entering various time intervals in each category are shown in the bottom panel of each plot.