FIGURE 1.
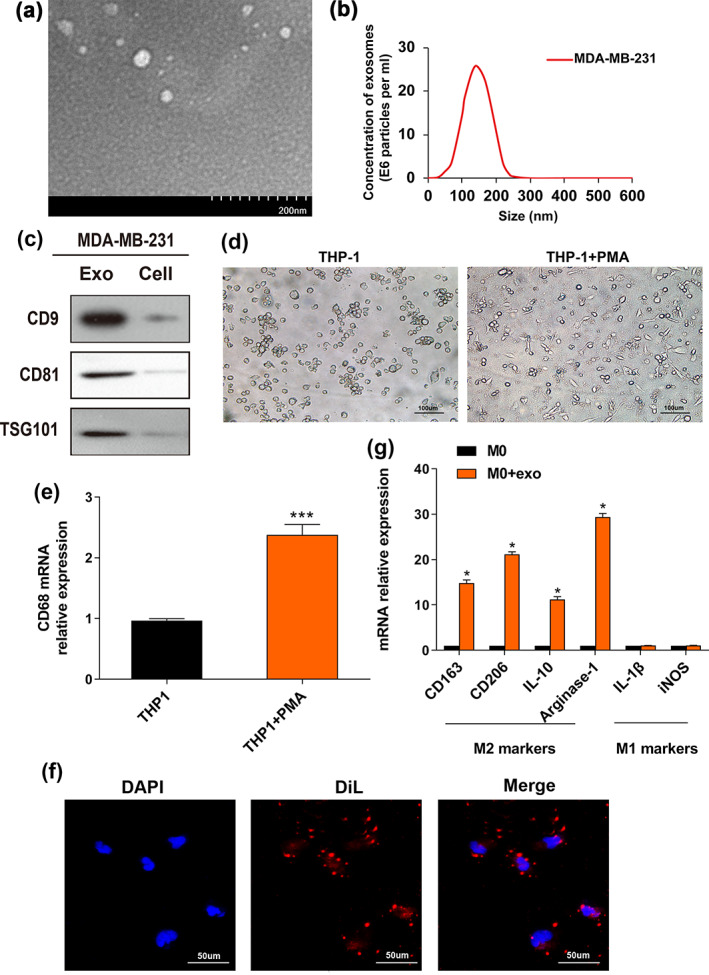
Breast cancer‐derived exosomes induce polarization of M2 macrophages. (a) Image of exosomes extracted from the conditioned medium of MDA‐MB‐231 cells was taken by electron microscopy. (b) The particle size distribution and concentration were estimated by the Nanosight LM10 system. (c) Exosomal markers (CD9, CD81 and TSG101) were evaluated by western blot (WB) assay in MDA‐MB‐231‐derived exosomes and cells. (d) THP‐1 cells were pretreated with PMA (100 ng/mL) for 24 h to generate M0 macrophages. Representative images of the two groups (THP‐1, THP‐1 + PMA) are shown. (e) qRT‐PCR was utilized to reveal macrophage marker CD68 expression. (f) Representative immunofluorescence images indicate the process of DiL‐labeled‐exosomes isolated from MDA‐MB‐231 internalized by macrophages. Scale bar, 50 μm. Original magnification ×200. (g) The M0 macrophages were incubated with PBS (control) or MDA‐MB‐231‐derived exosomes. qRT‐PCR was used to evaluate M2 markers (CD163, CD206, IL‐10, arginase‐1) and M1 markers (IL‐1β, iNOS) expression levels. The Student's t‐test was adopted to analyze the statistical significance of the difference between two groups, and one‐way ANOVA test was utilized to analyze multiple groups (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001).
