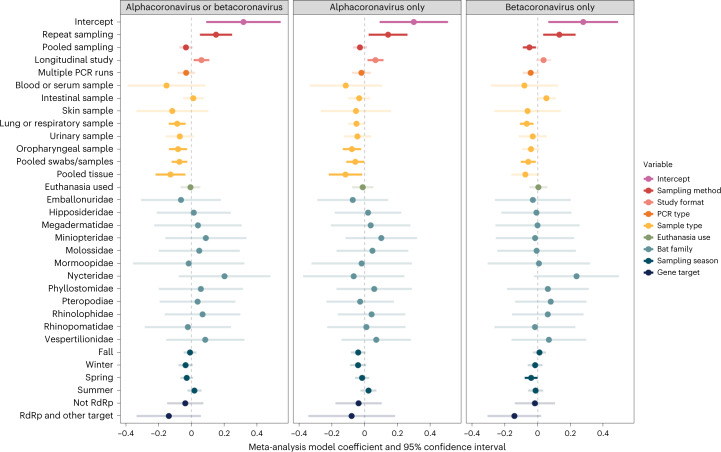
Fig. 4. Methodological and biological predictors of coronavirus prevalence in wild bats.
Phylogenetic meta-analysis model coefficients and 95% confidence intervals, estimated using REML for each of our three datasets. Colours indicate the nine variables included in each model (binary covariates for sampling season). Estimate confidence intervals are shaded by whether they cross zero (the vertical dashed line), with increased transparency denoting non-significant effects. The intercept contains the following reference levels: single sampling (sampling method); cross-sectional study (study format); single PCR (PCR type); faecal, rectal or anal sample (sample type); euthanasia not used (euthanasia use); Craseonycteridae (bat family); not fall, not winter, not spring and not summer (sampling season); and RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp) only (gene target). Sample sizes are 1,854 prevalence estimates for all coronaviruses, 1,553 prevalence estimates for only alphacoronaviruses and 1,428 prevalence estimates for only betacoronaviruses.