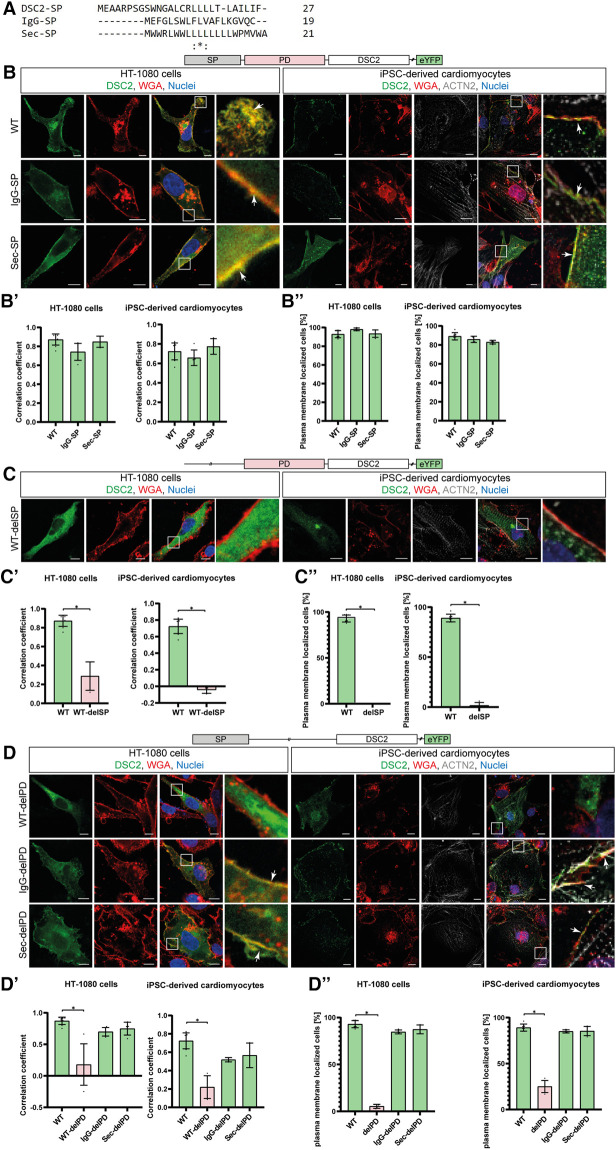
Figure 3.
Influence of alternative signal peptides (SP) on the localization of human DSC2. (A) Amino acid alignment of the three different SPs (DSC2/IgG/Sec-SP) using Clustal Omega (28). (B) Representative images of the construct localization with different SPs, (C) DSC2 lacking the SP and (D) constructs lacking the DSC2 prodomain (PD). HT-1080 cells and hiPSC-derived cardiomyocytes were transiently transfected with different eYFP-conjugated DSC2 constructs (green). Wheat germ agglutinin (WGA) conjugated to Alexa Fluor 633 (for HT-1080) and Alexa Fluor 647 (for hiPSC-derived cardiomyocytes) was used as a plasma membrane marker and is shown in red. Anti α-Actinin (ACTN2) antibody was used as a cardiomyocyte marker (grey). Nuclei were co-stained with 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI, blue). Arrows indicate the colocalization of DSC2 and WGA. Scale bars represent 10 µm. For each construct Pearson correlation coefficient (B’, C’, D’) was determined with a region of interest of 100 µm2. At least 100 cells were manually counted blinded for plasma membrane localization by an investigator (B’’, C’’, D’’). Nonparametric Kruskal-Wallis test followed by Dunn's multiple comparison was performed using GraphPad Prism Version 9.0. P-values <0.05 were considered significant (*). Mean values ± standard deviation are shown. Of note, wildtype and alternative SP constructs are localized at the plasma membrane. Without the SP or prodomain DSC2 is not properly localized. Interestingly, with IgG- or Sec-SP but lacking the PD the protein is localized at the plasma membrane as the wildtype.