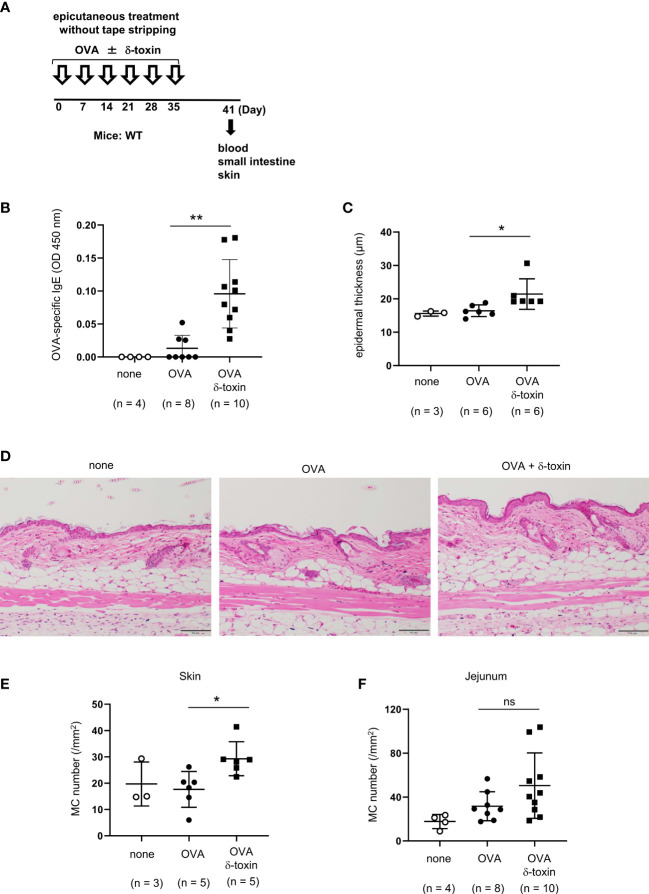
Figure 3.
δ-toxin present on the non-tape-stripped skin enhanced epicutaneous sensitization to food allergen in a murine model. (A) Experimental design for epicutaneous sensitization. WT mice were epicutaneously treated or not with OVA ± δ-toxin once a week for six weeks on the non-tape-stripped abdominal skin. On day 42, blood samples were obtained, and skins and small intestines were isolated. (B) Serum levels of OVA-specific IgE. (C) The thickness of epidermis. (D) Skin sections stained with hematoxylin and eosin (scale bars, 100 μm). (E, F) The numbers of mast cells in the (E) skin and (F) jejunum. (B, F) Data are pooled from two independent experiments. (C, E) Data are representative of two independent experiments. Means ± SD have been plotted. *, P < 0.05, **, P < 0.01. ns, not significant.