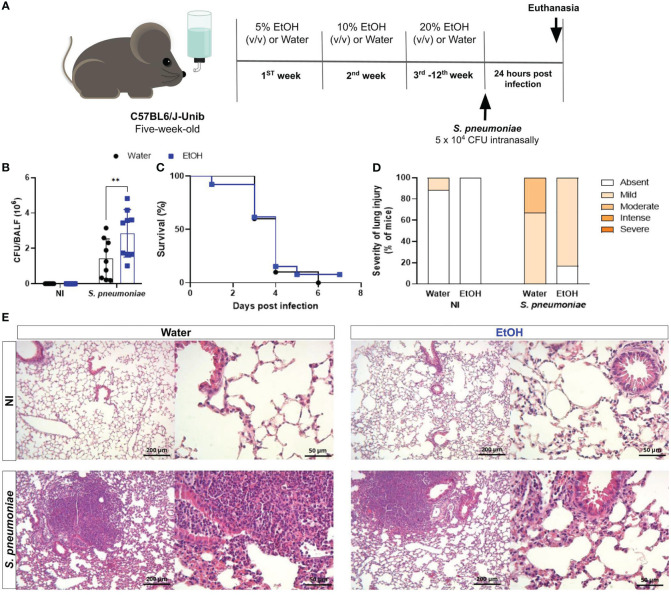
Figure 1.
Chronic alcohol exposure impaired bacterial clearance with no effects on survival rate after S. pneumoniae infection. (A) Methodological scheme of exposure to ethanol and infection. Five-week-old male C57BL6/J-Unib mice started the chronically exposure to ethanol with a 5% (v/v) alcoholic solution. Alcohol concentration doubled after one week until the third week and remained stable (20% v/v) at the end of treatment. After alcohol treatment, mice were infected with 5 x 104 CFU of S. pneumoniae. After 24h hours of infection, mice were euthanized. (B) Bacterial Load into the lungs after infection. (C) Lethality curves. (D) Percentage of mice with different severity of lung inflammatory lesions and (E) representative H&E stained lung section images under light microscopy at 10x and 40x magnification. Data are presented as the mean ± SD (6 to 9 mice per group). ** Significantly different (p < 0.01) by two-way ANOVA analysis test.