Figure 1.
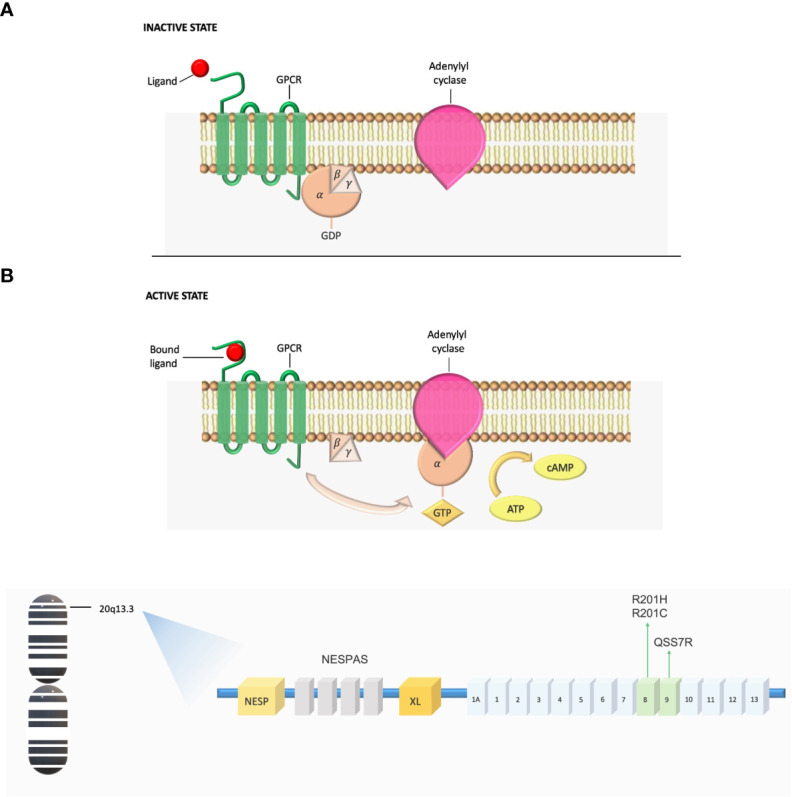
(A) Gs G-protein-coupled signaling dysregulation in FD/MAS. In the inactive state, the αβγ-heterotrimer is bound to GDP. After ligand binding, the GTP-bound α-subunit dissociates from the βγ-complex and activates adenylyl cyclase, leading to production of intracellular cyclic AMP and activation of protein kinase A and other downstream signaling pathways. ATP, adenosine triphosphate; cAMP, cyclic adenosine monophosphate; GDP, guanosine diphosphate; GPCR, G-coupled protein receptor; GTP, guanosine triphosphate. (B) Schematic of the GNAS complex locus. GNAS exons 1-13 encode Gsα. MAS arises from mutations in exon 8, where arginine 201 is converted to histidine (R201H) or cysteine (R201C), and mutations in exon 9, where glutamine is substituted for arginine (Q227R).
