Figure 2.
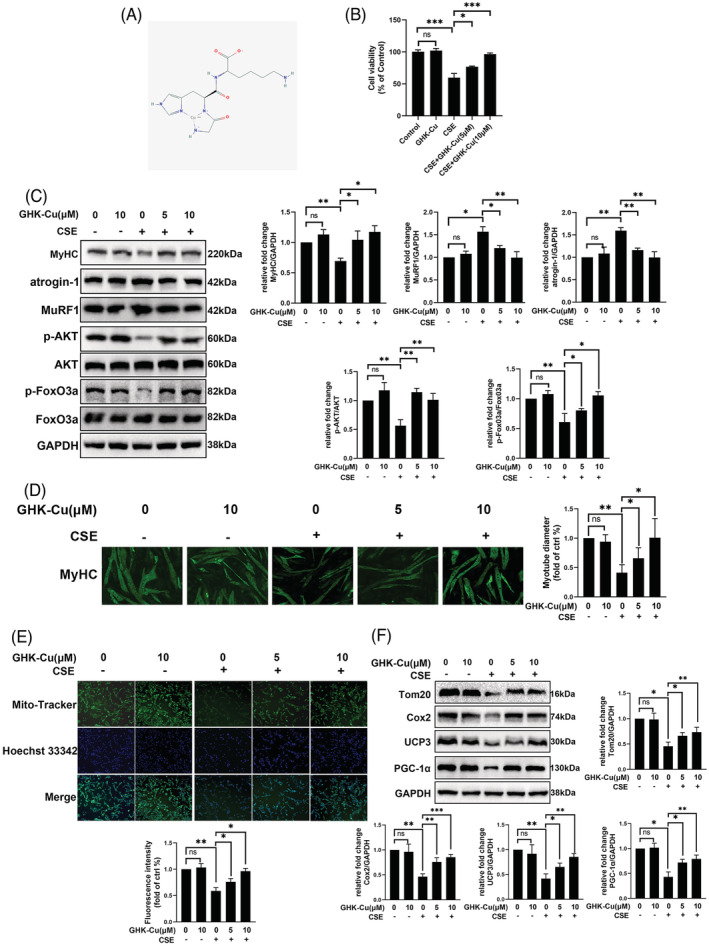
GHK‐Cu suppressed CSE‐induced C2C12 myotube injury alteration. (A) The structure of GHK‐Cu. (B) Cell viability of C2C12 myotubes treated with CSE and different concentrations of GHK‐Cu. (C) Western blot analysis of MyHC, atrogin‐1, MuRF1, AKT/FoxO3a levels in C2C12 myotubes, and relative intensity normalized to the expression of GAPDH. (D) Immunofluorescence staining showed that CSE‐treated myotubes had significantly smaller diameters compared with untreated myotubes. Meanwhile, GHK‐Cu treatment elevated diameters of myotubes compared with CSE‐treated myotubes in a concentration dependent manner (E)MitoTracker Green staining to assess the mitochondrial content of C2C12 myotubes. (F) Western blot analysis of Tom20, Cox2, ucp3, and PGC‐1α levels in C2C12 myotubes, and relative intensity normalized to the expression of GAPDH.
