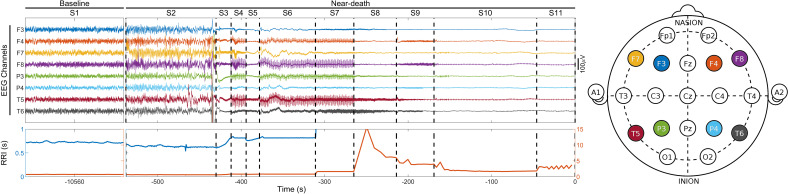
Fig. 1.
Select EEG channels from a 24-y-old comatose woman with cardiac arrest–induced anoxic injury on life support (S1 or baseline). The ventilator was removed at the start of S2, at which point high-frequency and high-amplitude activity develops. S2 ends with EEG suppression. The patient’s final heartbeat occurs at the end of S11, on the right. The location of the eight EEG electrodes, out of 19, is illustrated in the schematic on the right. The duration of heartbeat intervals (RRI) is shown on the bottom on a short (blue, on the left; 0 to 1 s) and long (brown, on the right; 0 to 15 s) timescales. Modified from figure S1A in Xu et al. (1).