Fig. 3.
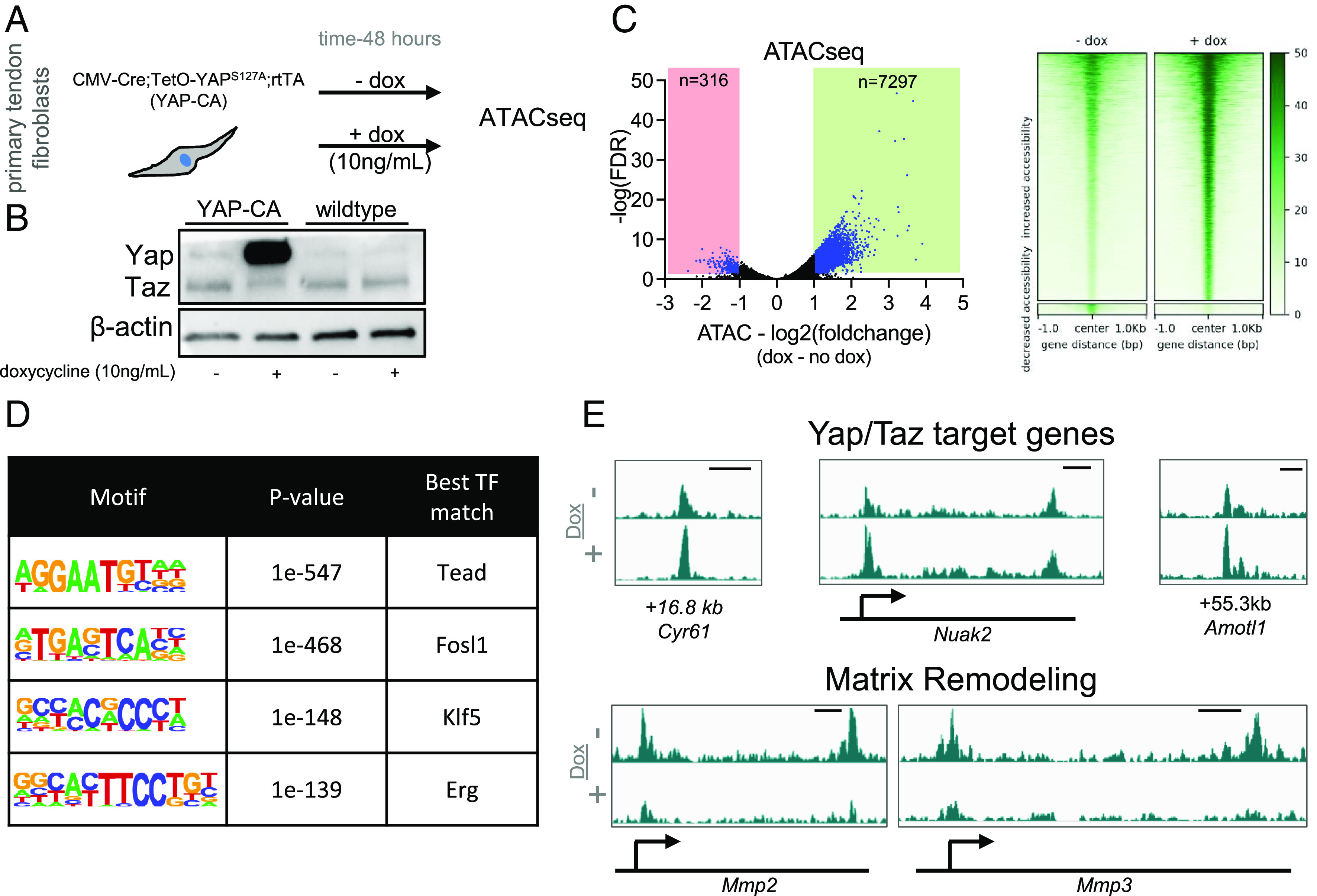
Yap overexpression maintains chromatin accessibility and reduces accessibility near matrix degradation genes. (A) Schematic showing approach to examine the role of Yap in maintenance of chromatin accessibility. (B) Western blot showing robust overexpression of Yap following 48 h of doxycycline treatment (10 ng/mL). (C) Volcano plot from ATACseq analysis showing differentially accessible genomic loci (adjusted P value ≤ 0.05 and a fold-change of ≤−1 or ≥ 1) in blue (n = 3 biological replicates). Heatmaps of chromatin accessibility changes following blebbistatin treatment are also shown. (D) De novo transcription factor motif enrichment analysis from the genomic loci identified in (C). (E) Representative chromatin accessibility tracks showing an increase of accessibility of Yap/Taz target genes (Cyr61, Nuak2, and Amotl1) and a reduction of accessibility of Mmp2 and Mmp3 following Yap overexpression. Genomic distance represents distance from gene TSS. Scale bar represents 1 kb.
