Fig. 2.
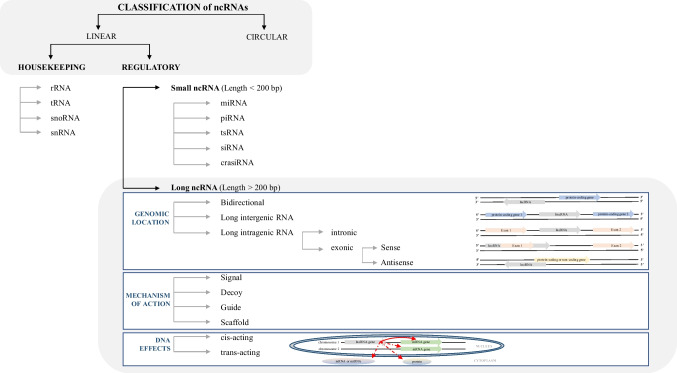
Schematic representation of a classification of non-coding RNAs based on their structure, function, length, genomic location, mechanism of action, and effects on DNA, emphasizing long non-coding RNAs; NcRNAs can be divided into linear or circular. According to their function, ncRNAs are recognized as housekeeping or regulatory. Housekeeping ncRNAs are constitutively expressed in each cell type, required for their viability and primarily regulating generic and essential functions of cells. The regulatory ncRNAs act as key regulators of various RNA molecules and gene expression at the epigenetic, transcriptional, and post-transcriptional levels. Based on their length, ncRNAs can be divided into small or long. LncRNAs can be genomically located between two protein-coding genes (intergenic lncRNAs), in an intron of a coding region (intronic lncRNAs), or within 1 kb of promoters and transcribed from the same promoter as a protein-coding gene yet in the opposite direction (bidirectional lncRNAs). Other lncRNAs can be transcribed either from the sense RNA strand of the protein-coding genes (sense lncRNAs) or the antisense RNA strand of a protein-coding gene (antisense lncRNA) might overlap one or several introns and/or exons. According to the mechanism of action, lncRNAs can be divided into four groups—signal, decoy, guide, and scaffold. Signal lncRNAs, with regulatory function, are expressed at a specific time and in a particular position in the cell as a response to stimuli. Signal lncRNAs can mediate the transcription of downstream genes alone or in combination with other proteins. Decoy lncRNAs can indirectly repress transcription, either binding to some functional proteins and blocking them from regulating DNA and mRNA or binding to miRNA competitively with mRNA and blocking the inhibitory effect of miRNA on mRNA. Guide lncRNAs are necessary to organize and locate some functional proteins at specific genomic loci to perform their functions. Scaffold lncRNAs are important in assembling multi-protein complexes in the target area. Moreover, lncRNAs can mediate epigenetic regulation via chromatin-modifying proteins in cis or trans manner. Cis-acting lncRNAs affect target genes located near the lncRNA gene on the same chromosome, while trans-acting lncRNAs affect target genes situated distal to the lncRNA gene, often in a different chromosome [22, 24, 26, 28, 30–32, 49–51]; Abbreviations used: crasiRNA, centromere repeat associated small interacting RNA; miRNA, microRNA; ncRNAs, non-coding RNAs; piRNA, piwi RNA; rRNA, ribosomal RNAs; siRNA, small interfering RNA; snoRNA, small nucleolar RNA; snRNA, small nuclear RNA; tRNA, transfer RNA; tsRNA, tRNA-derived small RNAs