Fig. 5.
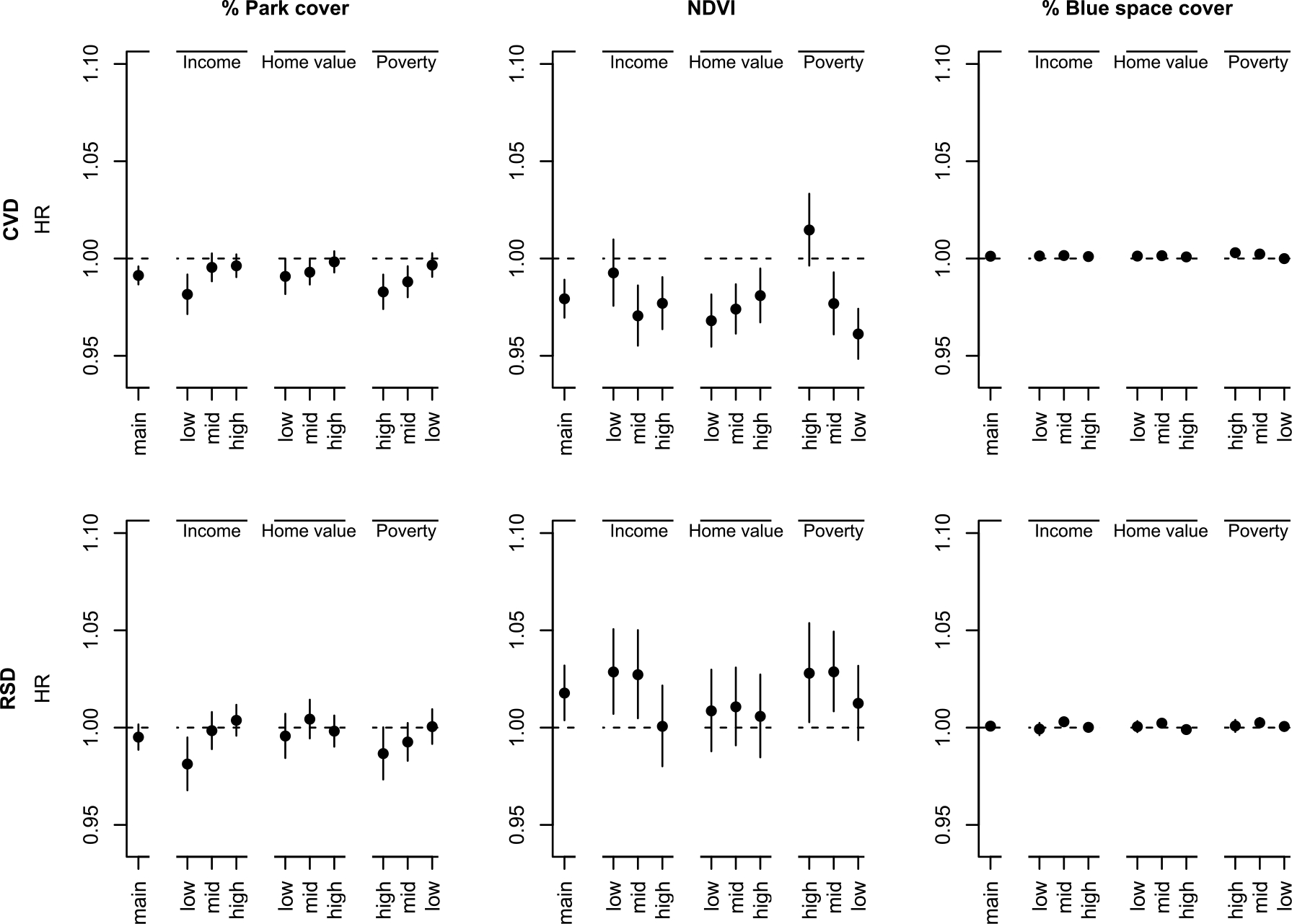
Associations of percent park cover, NDVI and percent blue space cover with CVD and RSD hospitalization in the urban population in stratified analyses by median household income, median home value and percent below the poverty level.a, b.
a Associations are expressed per IQR increase of the CVD hospitalization (full) cohort (IQR Percent park cover: 15.9, NDVI: 0.27, Percent blue space cover: 3.2). Models included park cover, NDVI, percent blue space cover and were adjusted for calendar year, region, U.S. census covariates, % ever smoked, summer temperature, summer specific humidity and summer total precipitation, an offset for total person-time and strata for all possible combinations of sex, race, Medicaid Eligibility, age at study entry (2-year categories), and follow-up year. b To define strata, we used the following quantiles (q33.3, q66.7) for the CVD cohort: median household income ($1000): 42.5, 62.4; median home value ($1000): 146.8, 276.8; percent below the poverty level (%): 6.5, 11.7; for the RSD cohort: median household income ($1000): 42.6, 62.5; median home value ($1000): 147.0, 276.7; percent below the poverty level (%): 6.5, 11.6.
