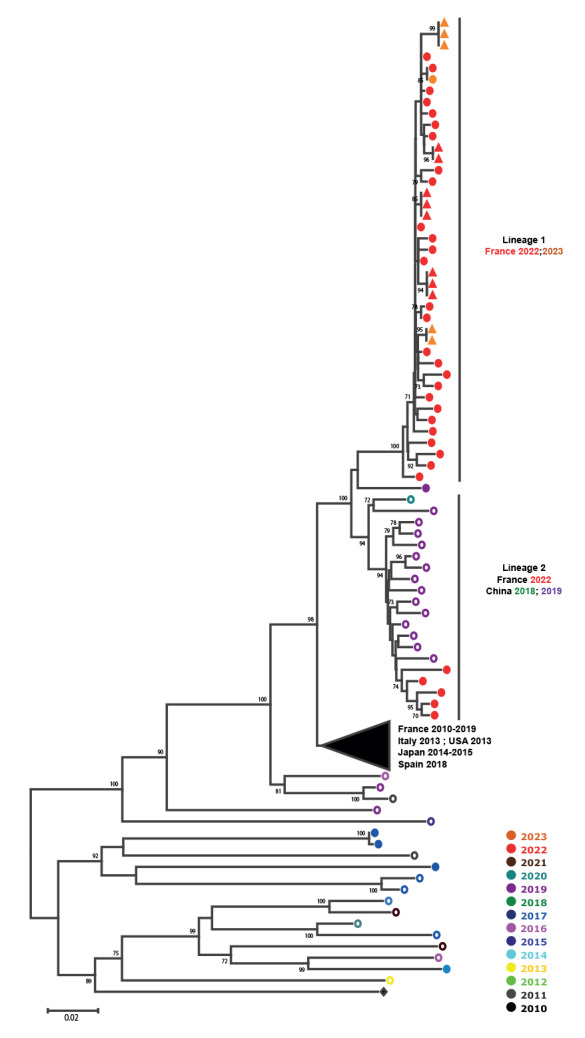
Figure 1.
Phylogenetic tree of echovirus 11 complete 1DVP1 sequences from neonatal and non-neonatal infections in France and other countries, 2010–2023 (n = 142)
MEGA: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis.
The phylogenetic tree was constructed by the neighbour joining method and evaluated with 1,000 bootstrap pseudoreplicates, using MEGA6. Only bootstrap values > 70% are indicated. Genetic distances were calculated with Tamura-Nei’s model of evolution and branch length is drawn to the indicated scale (proportion of nt substitution per site). The strains collected in patients with severe neonatal infection are labelled with a filled triangle. Strains collected in France (n = 104) between 2010 and 2023, accession numbers OQ927567, OQ923264, OQ927993–927997, OQ927998–928004, OQ969158-OQ969177, OQ971926-OQ971949; OR029978–030028) and in other countries (n = 37) (selected sequences among complete E-11 genomes available in GenBank, as of 28 April 2023) are labelled with a filled circle or empty circle, respectively. Year of isolation is colour coded. For clarity, the taxon names are not indicated in the tree. See Supplement 2 for taxon names. The French sequences from 2010 to 2023 were detected from samples from hospitalised patients in Orléans, Lyon, Clermont-Ferrand, Rouen, Cochin-Port Royal (Paris) and Necker-Enfants Malades (Paris) Hospitals, where the severe cases were reported.