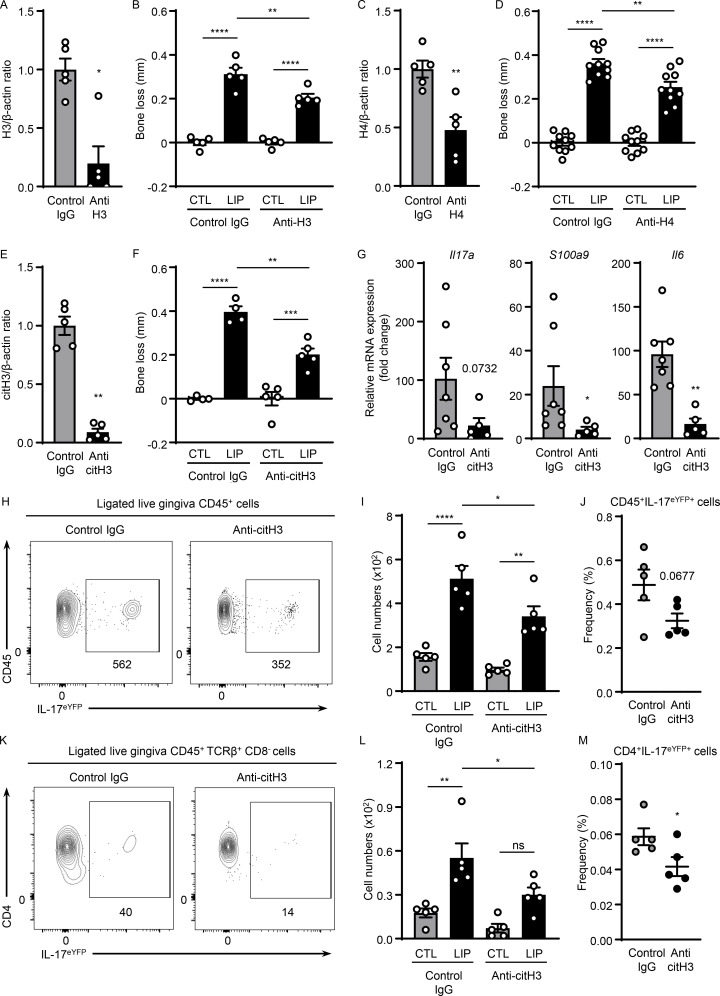
Figure 3.
Histones trigger periodontal inflammation and bone destruction. Mice with or without LIP were treated with isotype IgG, anti-H3, anti-H4, or anti-citH3. (A, C, and E) Western blot analysis for H3, H4, citH3, and β-actin in gingival tissues with or without LIP (6 d) in isotype IgG (n = 5), (A) anti-H3 (n = 5), (C) anti-H4 (n = 5), or (E) citH3 (n = 5) treated mice. Densitometric values for H3, H4, and citH3 were normalized against those of β-actin. (B, D, and F) Bone loss measurements in mice treated with isotype IgG (n = 4–10), (B) anti-H3 (n = 5), (D) anti-H4 (n = 10), or (F) citH3 (n = 4–5) treated mice, with or without LIP. (G) qPCR analysis for Il17a, S100a9, and Il6 in gingival tissues in mice treated with isotype IgG (n = 7) or anti-citH3 (n = 5, fold change 4 d after LIP shown for each treatment). (H–M) Flow cytometry analysis of gingival in IL-17acreR26ReYFP mice treated with isotype IgG (n = 5) or anti-citH3 (n = 5), with or without LIP. (H and K) FACS plot and graph indicating (I and L) numbers and (J and M) percentage of CD45+eYFP+ or CD4+eYFP+ cells. Data are representative of three (A–C, E, F, I, J, L, and M) or four (G) independent experiments. Graphs show the mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001. One-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparison test (B, D, F, I, and L) or unpaired t test (A, C, E, G, J, and M).