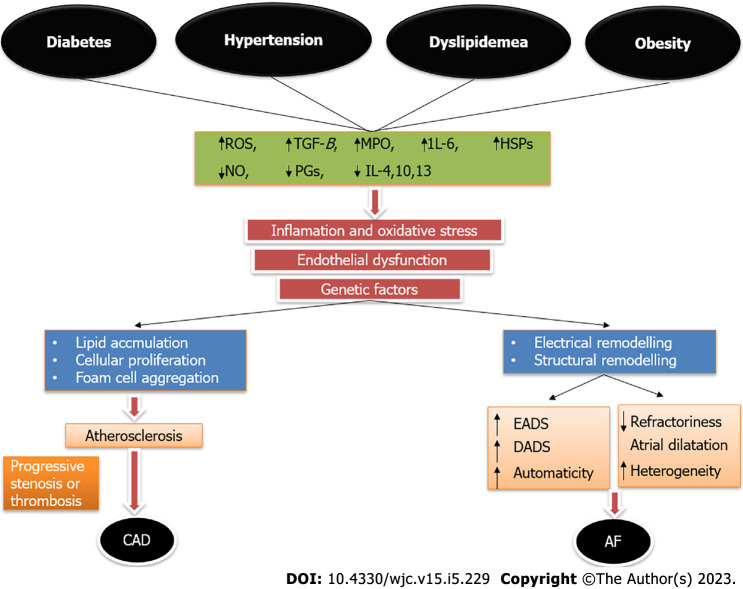
Figure 1.
Interplay of various common risk factors in the pathogenesis of coronary artery disease and atrial fibrillation. Variable genetic expression manifests as varied clinical phenotype in the form of either or both atrial fibrillation and coronary artery disease in an individual. AF: Atrial fibrillation; CAD: Coronary artery disease; EAD: Early after depolarization; DAD: Delayed after depolarization; HSPs: Heat shock proteins; IL: Interleukin; MPO: Myeloperoxidase; NO: Nitric oxide; PGs: Prostaglandins; ROS: Reactive oxygen species; TGF-β: Transforming growth factor beta.