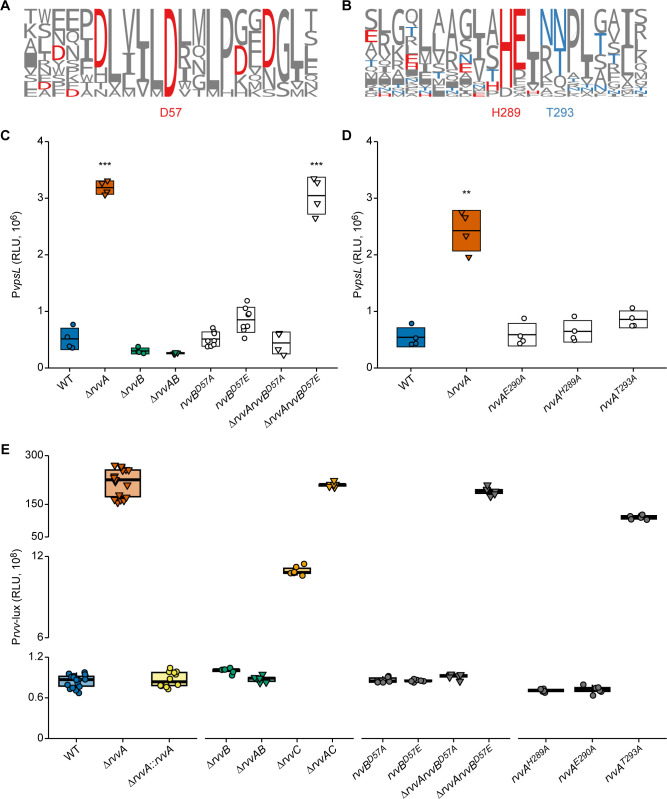
Fig 4. Impact of RvvAB phosphotransfer mutations on Rvv phenotypes.
(A) Seqlogo generated from amino acid sequence alignment of the REC domain of OmpR-like response regulators (RRs) in V. cholerae using ClustalO. The most conserved aspartate that was chosen for mutation is labeled (D57). (B) Seqlogo from amino acid sequence alignment of the HisKA DHp domain of Classic-type histidine kinases (HKs) in V. cholerae using ClustalO. Labels indicate the mutations generated in residues expected to impact kinase (H289) and phosphatase (T293) activity, respectively. (C-D) Promoter activity of the transcriptional fusion PvpsL-lux was measured from cells grown to exponential phase in the indicated strains. Individual data points (circles–RvvA present; triangles–RvvA deleted) of Relative Luminescent Units (RLU) are plotted with crossbars representing mean and standard deviation. Statistical significance was determined using a One-Way ANOVA and post-hoc Tukey’s multiple comparisons test. Means from individual biological replicates (n ≥ 6) were compared to that of wild type, and differences with an adjusted P value of ≤ 0.01 were deemed significant. **, P ≤ 0.001; ***, P ≤ 0.0001. (E) Promoter activity of the transcriptional fusion Prvv-lux was measured from cells grown to exponential phase in the indicated strains. Individual data points (circles–RvvA present; triangles–RvvA deleted) of Relative Luminescent Units (RLU) are displayed on top of a boxplot for each strain.