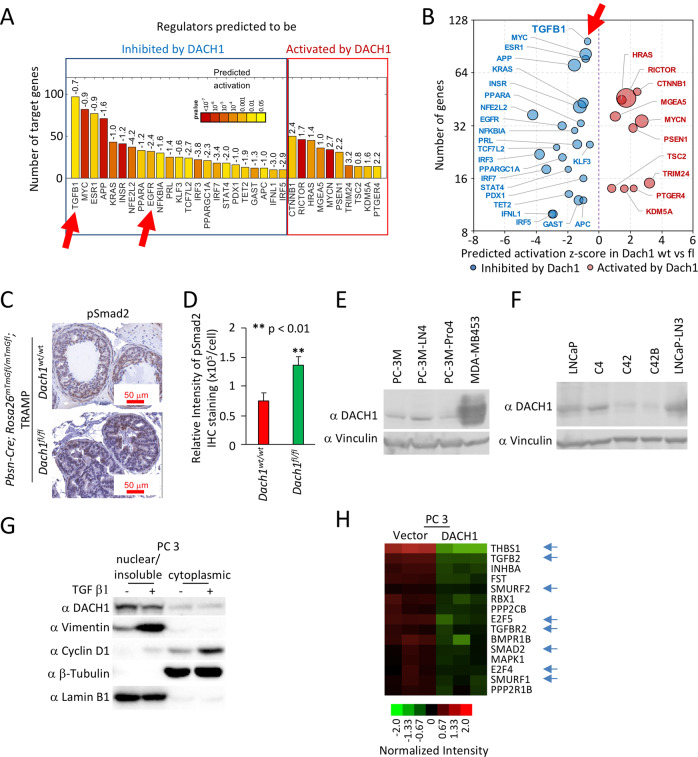
Fig. 4. Prostate-specific Dach1 gene deletion in TRAMP mice induces PIN lesions with increased TGFβ activity.
Genome-wide expression analysis of TRAMP Dach1+/+ vs. Dach1−/− PIN lesions was analyzed for enrichment of known targets of upstream regulators using Ingenuity Pathway Analysis (IPA) and represented as (A) barplot was calculated by IPA activation Z-score labeled and as (B) bubble plot with size of the bubbles proportional to –log10 p values. C IHC was conducted for SMAD activation using SMAD2P, quantitated and shown as (D) mean ± SEM (n = 15 for Dach1wt/wt mice, 3 separate mice, 5 views per mouse) (n = 10 for Dach1fl/fl mice, 2 separate mice, 5 views per mouse). E–G Western blot of either PCa cell lines for the presence of DACH1 (E, F) or (G) TGFβ-treated (10 ng/ml for 24 h) PC3 cells illustrating induction of nuclear vimentin and cytoplasmic cyclin D1. Protein loading controls are β-tubulin (a marker of cytoplasmic proteins) and Lamin B1 (a marker for nuclear protein enrichment). H Microarray-based gene expression analysis of PC3 cells stably expressing DACH1, showing restraint of genes mediating TGFβ signaling (shown with blue arrows), including reduction of TGFB2 and TGFBR2 [33].