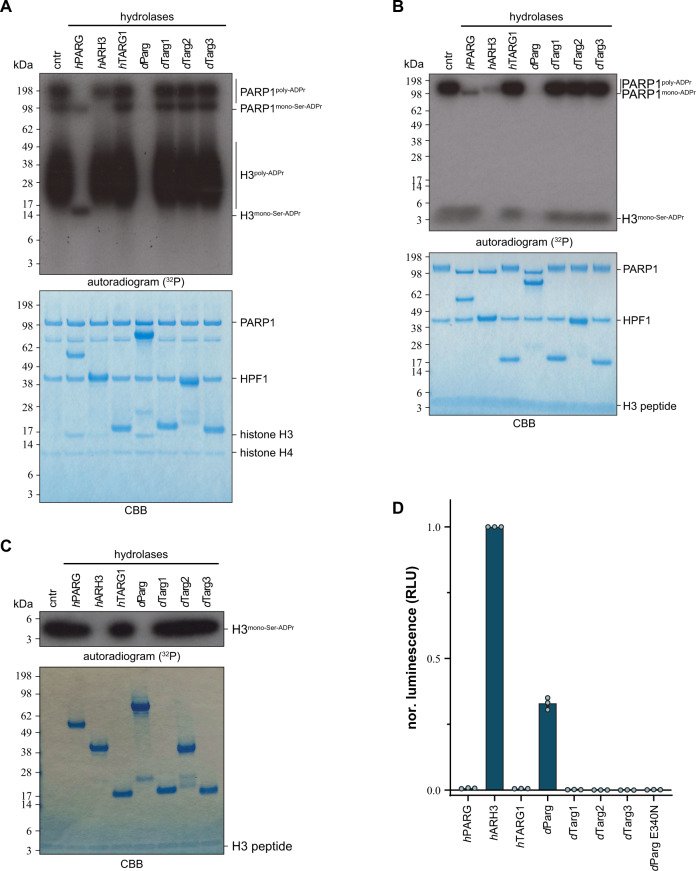
Fig. 7. dParg macrodomain catalyses mono-Ser-ADPr hydrolysis.
A Removal of poly-Ser-ADPr on automodified hPARP1 in the presence of hHPF1 and poly-Ser-ADP-ribosylated histone H3/H4 tetramer by human and Drosophila (ADP-ribosyl)hydrolases. The reaction was performed as in Fig. 5A, except histone H3/H4 tetramer was used instead of histone H3 peptide. Lower panel shows CBB stained SDS-PAGE of the proteins. The experiment was repeated independently three times with similar results. B Removal of poly-ADPr on automodified hPARP1 (0.5 μM), in the presence of hHPF1 (0.5 μM) and mono-Ser-ADP-ribosylated H3 peptide (aa 1–21, 0.5 µg) by human and Drosophila (ADP-ribosyl)hydrolases. Reactions were performed as described in Fig. 5A. Lower panel shows the CBB stained SDS-PAGE of the proteins. The experiment was repeated independently three times with similar results. C Removal of mono-Ser-ADPr on mono-Ser-ADP-ribosylated histone H3 peptide (aa 1–21) by human and Drosophila (ADP-ribosyl)hydrolases. Reactions were performed as described in Fig. 1A and peptide purified as described in Fig. 1B. Lower panel shows CBB stained SDS-PAGE of the proteins. The experiment was repeated independently three times with similar results. D Measurements of hydrolase activity of indicated hydrolases against synthetic histone H2B peptide mono-Ser-ADPr on S7 using the AMP-Glo assay (Promega). Samples are background corrected and normalised to hARH3. Data represent triplicate measurements of three independent experiments ± SEM.