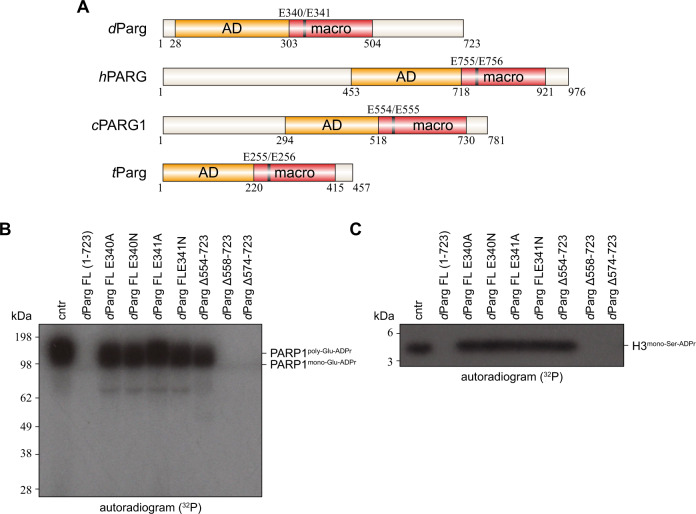
Fig. 8. The mono-Ser-ADPr hydrolase activity of dParg resides within its conserved active site.
A Schematic representation of the PARG domain architecture. The catalytic domain is composed of two subdomains; an accessory domain (AD, yellow) and macrodomain (macro, red). Domain boundaries are given below and the catalytic EE motif (black line) above the diagram. Abbreviation C. elegans PARG1, cPARG1; D. melanogaster Parg, dParg; Homo sapiens PARG, hPARG; Tetrahymena thermophila Parg, tParg. B Activity of dParg catalytic mutants and C-terminal truncations on poly-Glu-automodified hPARP1. Poly-Glu-automodified hPARP1 was obtained as described in Fig. 6C and subsequently supplemented with dParg WT or with indicated mutants. The experiment was repeated independently three times with similar results. C Activity of dParg catalytic mutants and C-terminal truncations on purified mono-Ser-ADP-ribosylated histone H3 peptide (aa 1–21). Mono-Ser-ADP-ribosylated histone H3 peptide (aa 1–21) was obtained as described in Methods and subsequently supplemented with dParg WT or with indicated mutants. The experiment was repeated independently three times with similar results.