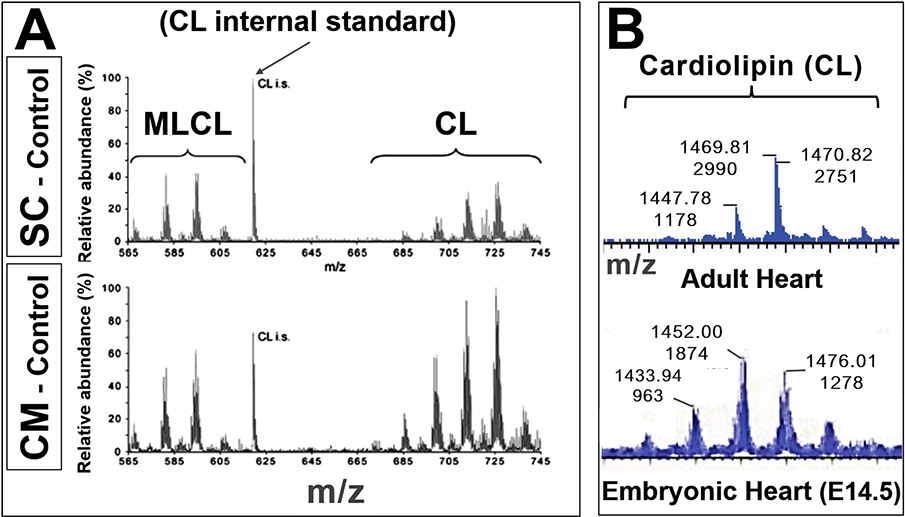
FIGURE 4. Cardiolipin species change during different developmental stages.
A) Cardiolipin (CL) and monolysocardiolipin (MLCL) in mouse embryonic stem cells (SC) and differentiated cardiomyocytes (CM). Lipid extracts of control (wildtype) cells were analyzed by mass spectrometry: Mass spectra of CL and MLCL are shown. The specific CL peaks at different m/z demonstrate differences in CL species between undifferentiated (SC) and differentiated (CM) cells, not simply a shift in MLCL:CL ratios. (Adapted from Acehan et al.64, with permission)
B) Mass spectra from wildtype mouse hearts: Adult (top) and E14.5 embryo (bottom: x-axes, or m/z axes, are aligned). The cardiolipin profiles (shifts in m/z [top numbers] and peak heights [bottom numbers]) indicate different cardiolipin species at different developmental stages. (Unpublished data, Phoon and Schlame labs)
These data illustrate the power of mass spectrometry to determine developmental lipidomics.