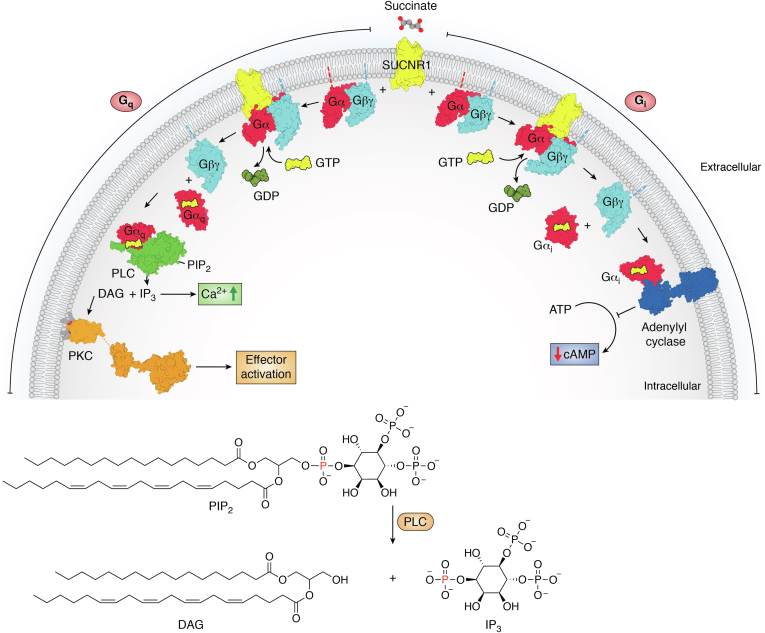
Figure 5.
Succinate-stimulated SUCNR1 signaling. SUCNR1 is a GPCR, or 7-TM receptor, that responds to stimulation by succinate (20). Like other GPCRs, SUCNR1 and the proteins in its downstream signaling pathways transmit information through conformational changes that can create or remove binding sites and/or change the catalytic activity of effectors. Although the pharmacology and signaling pathways are still in the process of being mapped, SUCNR1 (PDB 6RNK (225)) has been shown to couple to either Gq or Gi. In the figure, the SUCNR1-G protein complex is modeled from 6RNK (225) and either 1GOT (226) or 3SN6 (227), using 3SN6 as a guide to place the Gα and Gβγ subunits. Both Gq (modeled from 2BCJ (228) and 1GOT (226)) and Gi (modeled from 1GIA (229) and 1GOT (226)) are heterotrimeric G proteins containing Gαβγ subunits. SUCNR1 initiates G protein-dependent signaling by catalyzing GDP release from the Gα subunit. The binding of GTP, which is at a higher concentration in the cell, disassociates the GPCR–Gαβγ complex, releasing GTP-bound Gα (2BCJ (228) or 1GIA (229)) and Gβγ (from 1GOT (226) or 1TBG (230)). Classical Gαq (from 2BCJ (228)) signaling involves the activation of phospholipase C (PLC, 7SQ2 (231)), which catalyzes the cleavage of the membrane-associated PIP2 into two potent signaling molecules: IP3, which is soluble, and diacylglycerol (DAG), which remains membrane-attached. IP3 mobilizes intracellular Ca2+ while DAG activates protein kinase C (PKC, modeled from PDB 3PFQ (232) and PDB 7L92 (233)) via a C1 domain. The kinase activity of PKC leads to the activation of numerous signaling effectors. Among the most potent and best characterized effectors are the Ras-Raf-MEK-ERK signaling cascade, but other mitogen activated protein kinases (MAP kinases), and Src family kinases are downstream of PKC. Signaling via Gαi (PDB 1GIA (229)) inhibits adenylyl cyclase (AC, modeled from PDB 1CJK (234)), which normally converts ATP to cyclic AMP (cAMP). The inhibition of adenyl cyclase, therefore, decreases cAMP, which has a range of effects on cAMP-dependent processes. GPCR, G protein-coupled receptor; SUCNR1, succinate receptor 1.