Fig.1.
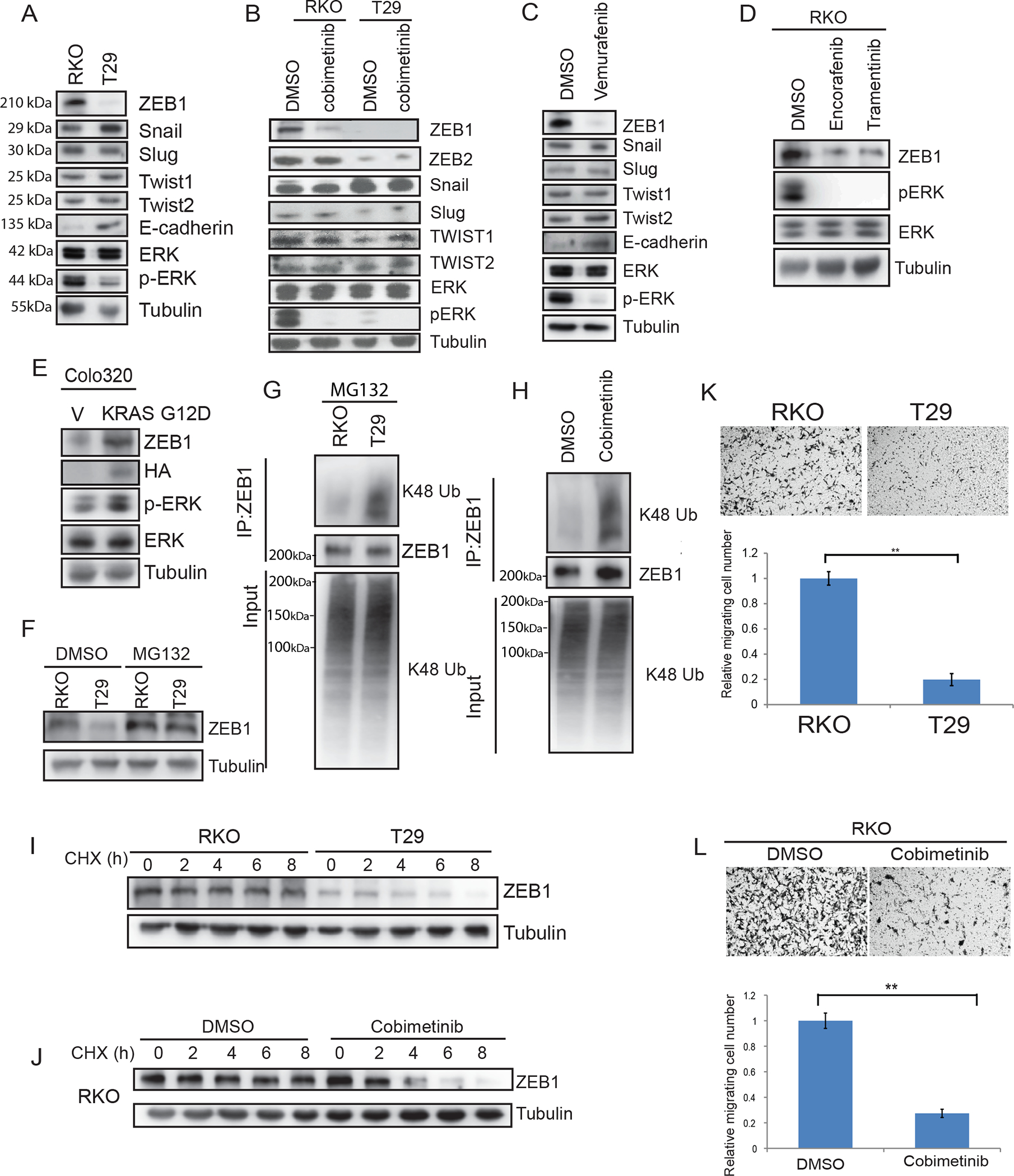
MEK-ERK signaling regulates ZEB1 protein stability and CRC cell migration.
A, Immunoblot analysis of expression of EMT transcription factors in isogenic CRC cell lines including parental RKO (BRAFV600E/V600E/wt) and T29 (BRAFwt/−/− ). B, Isogenic RKO cells treated with vehicle or MEK inhibitor cobimetinib (2 μM). C, EMT protein expression in RKO cells treated with BRAF inhibitor vemurafenib (5 μM) or vehicle. D, Detection of ZEB1 protein expression and p-ERK/ERK in RKO cells treated with BRAFV600E inhibitor encorafinib or MEK inhibitor trametinib (10 μM). (E), Colo320 cells transfected with mutant KRAS G12D. F, Analysis of ZEB1 expression in cell lines treated with the proteasome inhibitor, MG132. G-H, Cells were treated with MG132 and K48-linkage polyubiquitination of ZEB1 was analyzed in RKO and T29 cells (G), and in RKO cells treated with DMSO or cobimetinib (2 μM) [H]. I-J, Determination of ZEB1 protein half-life in RKO and T29 cells treated with cyclohexamide (I) and RKO cells treated with vehicle or cobimetinib (J). K, Analysis of isogenic RKO cell migration transwell assays and quantification of migrated cells. L, Analysis of RKO cell migration in presence of cobimetinib (2 μM) or vehicle by transwell assays and quantification of migrated cells in. Migrated cells were quantified from images (n=5) (K, L). Data are presented as mean ± SD. Student t test. **, p < 0.01.
