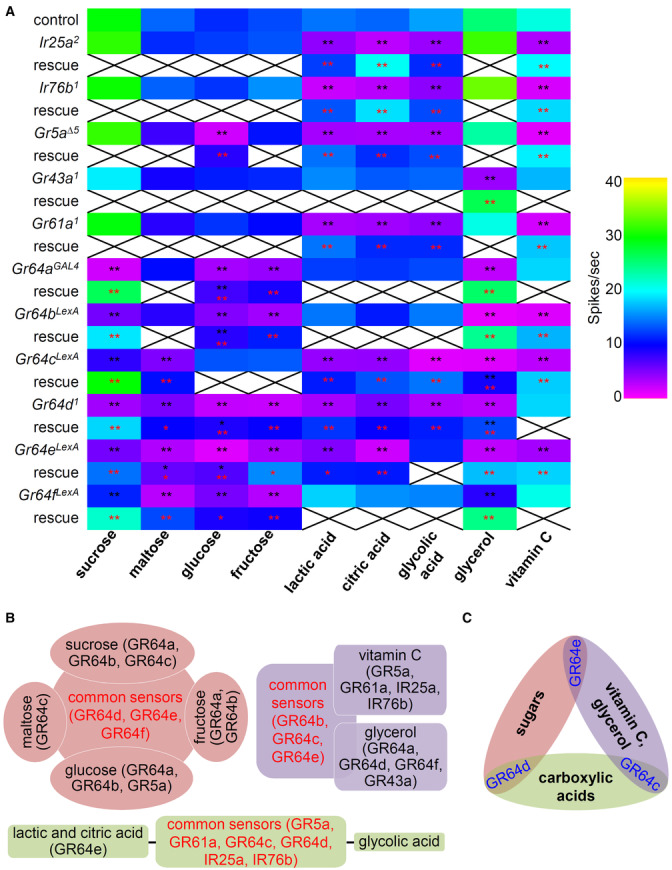
AElectrophysiology with the indicated mutants and control (w
1118
) in the presence of 50 mM sugars (sucrose, maltose, glucose, and fructose), 1% carboxylic acids (lactic acid, citric acid, and glycolic acid), and 50 mM vitamin C from L4 sensilla. The neuronal response to 10% glycerol was recorded from L7 sensilla. The defects of Ir25a, Ir76b, Gr5a, Gr61a, Gr64a, and Gr64f mutants were rescued by their own cDNA expression driven with their own GAL4s, while the rescue of Gr64b, Gr64c, Gr64d, and Gr64e were driven by Gr64f‐GAL4, n = 10–29. Multiple datasets were compared using a single‐factor ANOVA coupled with Scheffe's post hoc test. Black asterisks indicate statistical significance compared with the control. All the rescued flies had significantly increased spike activities; the red asterisks indicate statistical significance compared between the respective mutant and the rescued flies. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01.