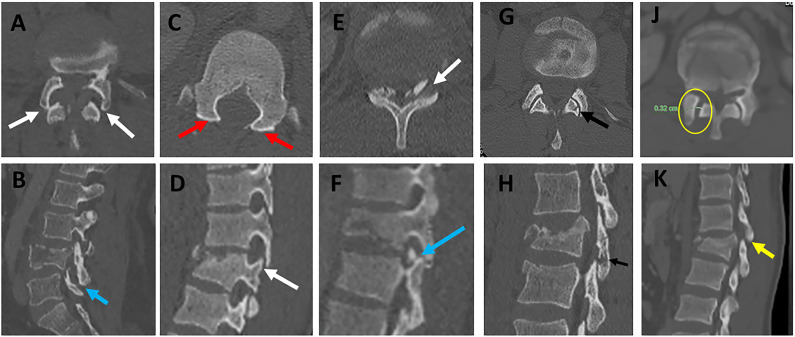
Figure 10.
Various patterns of facet diastasis in CT. Facet dislocation (A, B ) seen in CT axial images show (2 white arrows, A) and sagittal CT image (blue arrow, B); Facet Subluxation (C, D ) seen in CT axial images as bilateral naked facet sign (2 red arrows, C) and sagittal CT image as a vertical distraction (white arrow, D); Displaced facet fracture (E, F) seen in CT axial images (white arrows, E) and sagittal CT image as a displaced fracture of the left superior articular facet (blue arrow, F); Non-displaced facet fracture (G, H) is seen in CT axial images (black arrow, E) and sagittal CT images as a non-displaced fracture of the left inferior articular facet (black arrow, F); Facet joint widening (J, K) is seen in CT axial images as widening of the facet joint > 3mm with the preserved alignment of articular surfaces (yellow circle, J) and sagittal CT images (green arrow, K). Abbreviations: CT, computed tomography.