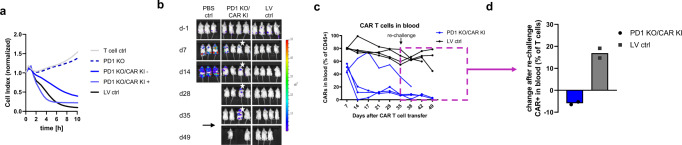
Fig. 2. Inducible CAR T cells are functional in vitro and in vivo.
a Activated engineered feedback loop CAR T cells show faster in vitro killing compared to rested counterpart. Graph shows impedance measurement as a read out of antigen specific killing of target cells. Untransduced T cells (neg control), PD1 KO only T cells (PD1 KO), CAR T cells LV-transduced (LV control) as well as rested (PD1 KO/CAR KI -) and polyclonally restimulated (PD1 KO/CAR KI +) engineered feedback loop CAR T cells were used. Experiment shows single data points derived from median of quadruplicates. b Engineered feedback loop CAR T cells are as functional as state-of-the-art CAR T cell product in an in vivo mouse model. Tumor was detected using IVIS bioluminescence measurements. Luminescence images from one representative experiment are shown. Arrow indicates re-challenge of mice. c Engineered feedback loop CAR T cells can help restore B cell compartment after complete tumor eradication. CAR T cell content in blood of each individual mouse was calculated using cell frequencies measured via flow-cytometry. Cells were pre-gated on living lymphocytes. Box highlights cell frequencies after B cell re-challenge (d35). Mouse with prolonged tumor burden highlighted by star in b and c. Each line represents corresponding mouse. d B cell re-challenge on day 35 leads to rapid increase in LV-transduced CAR T cell content while engineered feedback loop CAR T cell content remains unchanged. Delta calculated based of CAR T cell frequencies between day 28 (tumor clearance) and day 45 (post re-challenge).