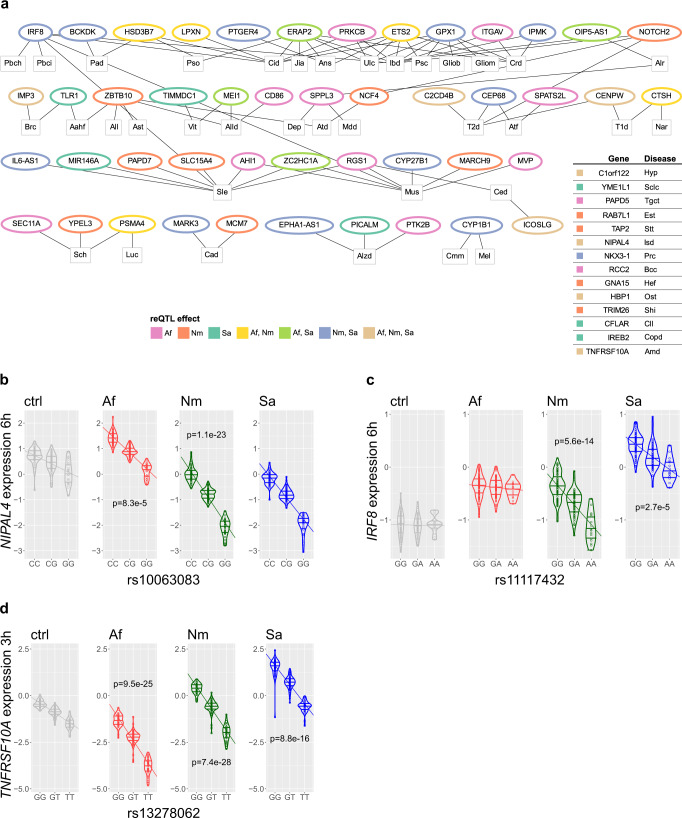
Fig. 6. reQTLs and regulated genes that correspond to disease-associated GWAS-SNPs.
a Disease-associated genome-wide association study single-nucleotide polymorphisms (GWAS-SNPs) in high linkage disequilibrium (LD) (r2 > 0.8) with response expression quantitative trait loci (reQTL) in pathogen-exposed monocytes. reQTL-regulated genes are connected to diseases by lines. Inserted table lists reQTL-regulated genes connected to only one disease. Colors: exposure to different pathogens. b–d Allele-dependent differences in expression of NIPAL4, IRF8 and TNFRSF10A following pathogen exposure. Corresponding reQTLs are in LD with GWAS-SNPs for b psoriasis, c primary biliary cholangitis, inflammatory bowel disease, systemic lupus erythematosus, multiple sclerosis or d age-related macular degeneration. For IRF8 and TNFRSF10A only the top SNP for one condition with strongest p-value is shown. Ctrl: unstimulated, Af: A. fumigatus, Nm: N. meningitidis, Sa: S. aureus. Bonferroni corrected p values from z test of differences in regression coefficients to unstimulated control (ctrl) are indicated. List of disease-associated GWAS-SNPs with reQTL effects in stimulated monocytes with all associations of reQTLs and GWAS diseases and disease abbreviations is provided in Supplementary Data 7. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.