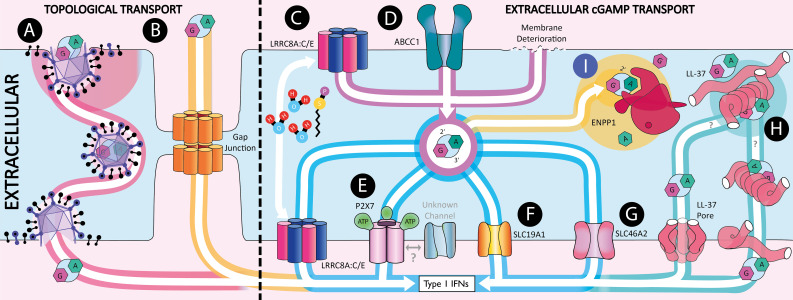
Figure 2.
Extracellular 2’3’-cGAMP transport. Schematic showing the mechanisms by which 2’3’-cGAMP can be transferred between cells. (A) Within viral particles. (B) Through gap junctions. (C) Import and export through LRRC8A:C heterodimers which are activated by hypotonicity and Sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P). (D) Export through ABCC1. (E) Transport through the ATP gated pore P2X7. (F) Import through SLC19A1. (G) Import through SLC46A2. (H) 2’3’-cGAMP shuttling by LL-37. (I) 2’3’-cGAMP hydrolysis by ENPP1.