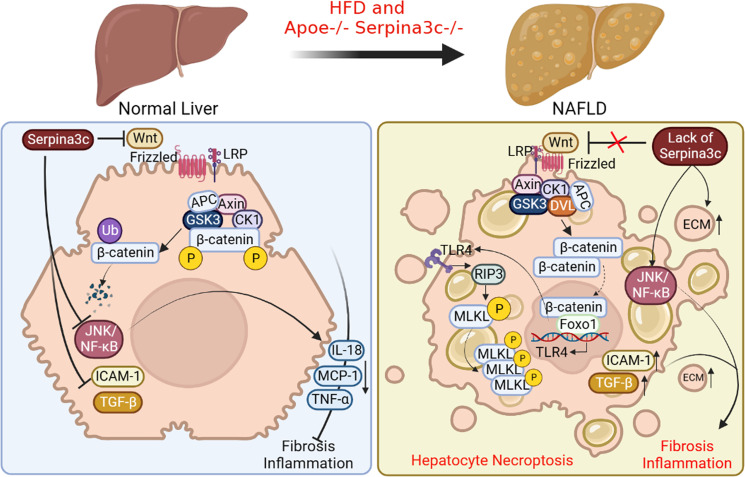
Figure 5.
The beneficial roles of Serpina3c in NAFLD. In normal liver, Serpina3c can inhibit Wnt/β-catenin signal pathway, promotes ubiquitination-mediated degradation of β-catenin, inhibits JNK/NF-κB signal pathway, reduces the expression of inflammatory cytokines interleukin 18 (IL-18), MCP-1, TNF- α, and decreases the expression level of intercellular adhesion molecule 1(ICAM-1) and TGF-β. These will reduce liver inflammation and fibrosis. However, in the NAFLD livers of Apoe and Serpina3c double knockout mice fed with HFD, due to the lack of Serpina3c, Wnt/β-catenin signal pathway could not be inhibited, making the entry of β-catenin into the nuclei, which interacts with Foxo-1 to activate TLR4 transcription. Increased expression of TLR4, and activation of downstream receptor interaction protein 3 (RIP3) and phosphorylation mixed lineage kinase domain-like pseudokinase (MLKL) will then induce hepatocyte necroptosis. The deletion of Serpina3c leads to the activation of JNK/NF-κB signal pathway and the increase of the expression of ICAM-1 and TGF-β. The content of extracellular matrix (ECM) will be increased. Together, these lead to more severe inflammation and fibrosis in the liver. (Created with BioRender.com).